📈 Introduction
In late 2025, USA Doubles tariffs on Indian goods surged to an effective 50% for wide baskets of merchandise, jolting exporters, MSMEs, and supply chains that had spent a decade integrating with American buyers. The shock came at a delicate moment for India’s manufacturing push—just as firms scaled up textiles, gems & jewellery, auto components, processed foods, and chemicals for global markets. As buyers in the United States scrambled to renegotiate, and the rupee weakened amid risk‑off flows, Indian companies were forced into a fast re‑think: hold margins and risk lost volumes, or slash prices and bleed cash. This India‑first explainer maps which sectors hurt most, how pricing and logistics have shifted, where opportunities still exist, and what playbooks—from hedging to market diversification—can protect jobs and growth while the storm lasts.
Meta description: India’s 2025 guide to U.S. tariffs doubling to 50%—sector damage, rupee effects, pricing math, case studies, mitigation, and export diversification strategies.
🧭 What changed—and why it matters for India
The tariff regime changed in two steps in mid‑2025, taking effective duties on many Indian exports to 50% in the U.S. market. For India, this matters because the U.S. is both a high‑margin buyer and a standards trend‑setter: once a line loses shelf space in America, it often loses global visibility, credit cycles shift, and working capital tightens across supplier clusters. The blow lands heaviest where India is labor‑intensive and price‑sensitive—apparel, leather, gems & jewellery, shrimp/seafood, select chemicals, and wood/furniture—while pharmaceuticals and parts of electronics appear relatively insulated for now. With shipping and insurance premia also volatile, the landed‑cost gap against competitors can widen faster than catalogues can be re‑priced.
🧮 Tariff arithmetic: how a 25% top‑up doubles pain
- 🔢 Compounding effect: If a line already faced 25%, an added 25% doesn’t sum to 50% arithmetically in contracts—it compounds into a much bigger landed‑cost wedge once you stack logistics, insurance, and importer markups. A ₹100 ex‑factory that shipped at ₹120 CIF can now land near ₹150–₹160 equivalent after high‑street margins—pricing many SKUs off the shelf.
- 🧾 Margin math: Labor‑heavy verticals run on 8–12% net margins in good times. Even after a weaker rupee cushions 2–4%, the tariff wedge wipes out profits unless the buyer raises sticker prices or the exporter offers deep discounts. Neither is easy in an environment where U.S. retailers are guarding inventory turn and value perception.
- 📦 Contract cadence: Many Indian exporters work on quarterly or semi‑annual order cycles. A mid‑season tariff shock leaves in‑pipeline shipments exposed; renegotiation windows open only after the current purchase orders clear, creating a gap quarter where plants run under‑utilized.
Related read: Export Shock—India Faces $33 Billion Loss Amid U.S. Tariffs
🧳 Who gets hit first: product categories with maximal exposure
- 👗 Textiles & apparel: India’s core strength in cotton knits, home textiles, and fast fashion basics collides with U.S. discounters’ obsession with price points (e.g., $9.99 tees, $14.99 joggers). A 50% duty forces a wholesale rethink of pack sizes, fabric GSM, and automation to extract cost.
- 💎 Gems & jewellery: Diamond cutting/polishing clusters in Surat and jewellery units in Mumbai/Jaipur rely on U.S. bridal and holiday cycles. With tariffs, buyers may pivot to lab‑grown diamonds or shift finishing to low‑duty hubs.
- 🦐 Seafood (shrimp): India’s farmed vannamei exports are price‑elastic; a tariff wedge triggers menu re‑engineering at U.S. restaurant chains—impacting Andhra and Odisha farmer incomes.
- 🚗 Auto components: Traditionally competitive in castings, forgings, and wiring harnesses, Indian suppliers could lose new platform awards if U.S. OEMs can’t absorb the landed‑cost jump.
- 🧴 Specialty chemicals: Where India sells intermediates into U.S. formulations, buyers can rush to Mexico/Vietnam/EU for interim fills; restarting those relationships later is sticky.
🗺️ Geography of pain inside India
- 🧵 Tiruppur/Ludhiana (knits), Panipat/Karur (home textiles), Surat (diamonds), Jaipur (gem‑set jewellery), Moradabad (metalware), Jalandhar (leather goods), Kutch (ceramics), Rajkot (engineering), Srivardhan‑coast/Andhra (shrimp), Vapi/Ankleshwar (chemicals).
- 🛠️ Ancillary jobs—packing, embroidery, finishing, logistics—see faster layoffs than core skilled roles, hitting women’s employment and migrant workers first.
🧠 Comparison — sector stress, pricing levers, near‑term prognosis
| 🧩 Sector | ⚙️ Pricing levers that still work | 🔭 6–12 month prognosis |
|---|---|---|
| Textiles/Apparel | Fabric re‑engineering, bundle packs, duty‑free input sourcing | Medium‑high stress; partial demand substitution |
| Gems & Jewellery | Lab‑grown lines, design up‑tiering, duty‑suspended finishing hubs | High stress; luxury may absorb, mass lines weaken |
| Seafood (shrimp) | Menu redesign, value‑added packs, channel shift to EU/ASEAN | High stress; farmgate prices under pressure |
🧰 Company playbooks to survive the tariff wave
- 🧮 Re‑cost every SKU: Split by duty‑paid and duty‑suspended options (e.g., U.S. FTZs, bonded warehouses), drop long‑tail SKUs, double down on winners.
- 🌏 Diversify buyers: Reweight towards EU, GCC, ASEAN, and Japan where standards are compatible and logistics cycles are predictable.
- 💱 Hedge policy: Use forwards/options to lock FX; negotiate tariff‑sharing with top buyers for bridge quarters.
- 🧑🤝🧑 Consortium selling: Cluster‑level branding can shift buyer perception from price to craft/quality, slowing the race to the bottom.
- 🧪 Product pivots: Move up the value chain (e.g., functional fabrics, green chemistry, ready‑to‑cook shrimp formats) where buyers defend shelf space.
Deeper strategy: How India Can Diversify After Trump Tariff Shock: ASEAN, EU, and Beyond
🧠 Pricing math example—home textiles to a U.S. big‑box chain
Consider a ₹300 ex‑factory cotton bedsheet set. Add ₹30 packaging, ₹25 inland freight, ₹45 ocean freight/insurance in peak. Pre‑tariff, U.S. duty + handling took ~₹50, giving a landed near ₹450 before retailer margin. With effective 50% duties, the landed cost can jump to ₹525–₹560 equivalent. If the retailer must hold the $29.99 price point, either the exporter takes the hit, the retailer shrinks specs (lower thread count), or the line is shelved. The realistic move is a mid‑spec relaunch with bundle offers and promotion weeks while shifting volume to EU/GCC.
🧭 FX and rates: what a weaker rupee really offsets
- 💱 Cushion, not cure: A 2–5% rupee depreciation softens the blow but can’t plug a 25‑point tariff wedge. Exporters should bank FX gains to fund productivity upgrades, not to underwrite deep discounts.
- 🏦 Working capital: Higher interest rates for risk assets plus stretched receivables tighten liquidity. Negotiate factoring lines and credit insurance where viable.
Market lens: Market Fallout—Trump’s Tariffs Send Rupee Weak, Shake Investor Sentiment
🧪 Case story — Tiruppur knitwear cluster’s fast pivot
A mid‑sized Tiruppur exporter with 1,100 workers sells basics to two U.S. discount chains. Post‑tariff, U.S. POs drop 30%. The firm re‑engineers its core tee with a lighter GSM cotton‑poly blend and three‑pack bundling, then targets Germany and UAE with the new spec. It also signs a shared freight agreement with two peer factories to keep box rates predictable. In two quarters, U.S. share falls from 62% to 35%, but overall volumes stabilize and margins recover to 7.5%.
🧪 Case story — Surat diamonds go hybrid
A Surat cutting unit faces canceled U.S. bridal orders. It spins up a lab‑grown capsule line with Jaipur settings, runs virtual try‑on, and ships via a duty‑suspended finishing hub. The U.S. share reopens at a lower base, while Canada/GCC absorb premium SKUs. Employment holds, with women polishers re‑skilled for QC of new stones.
🧠 Employment and social impact
- 👩🏭 Women‑led roles in stitching, finishing, and packaging take first hits. State skilling missions should subsidize re‑training in quality control, machine operation, and export documentation.
- 👨🌾 In shrimp belts, lower farmgate prices ripple into feed and credit stress. Crop insurance designs that account for trade shocks can prevent exits.
- 🧳 Migrant workers in apparel and leather hubs need hostel and health support to avoid reverse migration that breaks cluster productivity.
🧮 Comparison — buyer reactions and how exporters should respond
| 🛒 Buyer behavior in the U.S. | 🇮🇳 Exporter response | 🧭 Why it helps |
|---|---|---|
| Trade down to private labels, essentials | Offer OEM white‑label and bundle packs | Defends shelf space and volume |
| Shorter order cycles | Agile production + fabric/yarn booking | Reduces inventory risk for both sides |
| Risk diversification across countries | Co‑manufacture with trusted peers | Keeps partial share while tariffs persist |
🧭 State‑level responses that matter now
- 🏭 Plug‑and‑play sheds in affected clusters for quick relocations and process upgrades.
- 💸 Interest subvention for export working capital tied to productivity KPIs.
- 🚢 Port priority windows for clusters with seasonal demand (apparel/seafood) to cut dwell time.
- 🧑⚕️ Women’s safety & creches near factories to retain the skilled base.
Policy angle: Retaliation or Diplomacy—What India Can Do Amid Rising U.S. Tariffs
🧩 Category deep dives—how specific lines can fight back
👚 Textiles & apparel—from commodity to capability
Textiles feel the quickest demand shock because U.S. retailers buy to price points and seasons. The way out is capability migration: thicker blends, functional finishes (anti‑odor, moisture wicking), digital printing for micro‑drops, and automation in cut‑and‑sew to protect margins. Mid‑tier mills can also build captive design pods to pitch curated collections rather than bulk basics—nudging conversations from price to sell‑through. Finally, traceability and sustainability metrics (water use, dye effluents) can open doors in EU/Japan, de‑risking the U.S. shock.
💎 Gems & jewellery—narrative, not just price
The U.S. tariff narrows bands for impulse jewellery purchases. Indian houses can up‑tier designs, lean into lab‑grown for price resilience, and keep custom options for American independents. Storytelling—artisan craft, ethical sourcing, and re‑use/re‑set programs—builds defensibility. Virtual try‑on and store‑in‑store tie‑ups with North American retailers can protect presence while negotiations evolve.
🦐 Seafood—value‑added or value‑lost
If tariff‑induced menu re‑pricing is unavoidable, Indian players should pivot to value‑added packs—marinated, ready‑to‑cook, batter‑coated—and raise EU/GCC exposure where foodservice is price‑sensitive but rules allow managed spec changes. Cold‑chain collaboration among exporters can raise container utilization and stabilize farmgate demand.
⚙️ Auto components—keep the platforms
Component makers need to protect design‑in positions for 2026–27 vehicle platforms. That means co‑investing with U.S. Tier‑1s in process validation and PPAP updates that balance cost and reliability. For near‑term cash flow, widen aftermarket SKUs in Latin America and Africa while defending OE relationships through engineering concessions instead of price cuts.
🧪 Specialty chemicals—stickiness via formulation support
Indian chemical exporters should offer process documentation, alternate grades, and stability data to make substitution harder. Joint lab work with clients and dual‑sourcing within India helps anchor orders, while Mexico/EU provide bridge markets for displaced volumes.
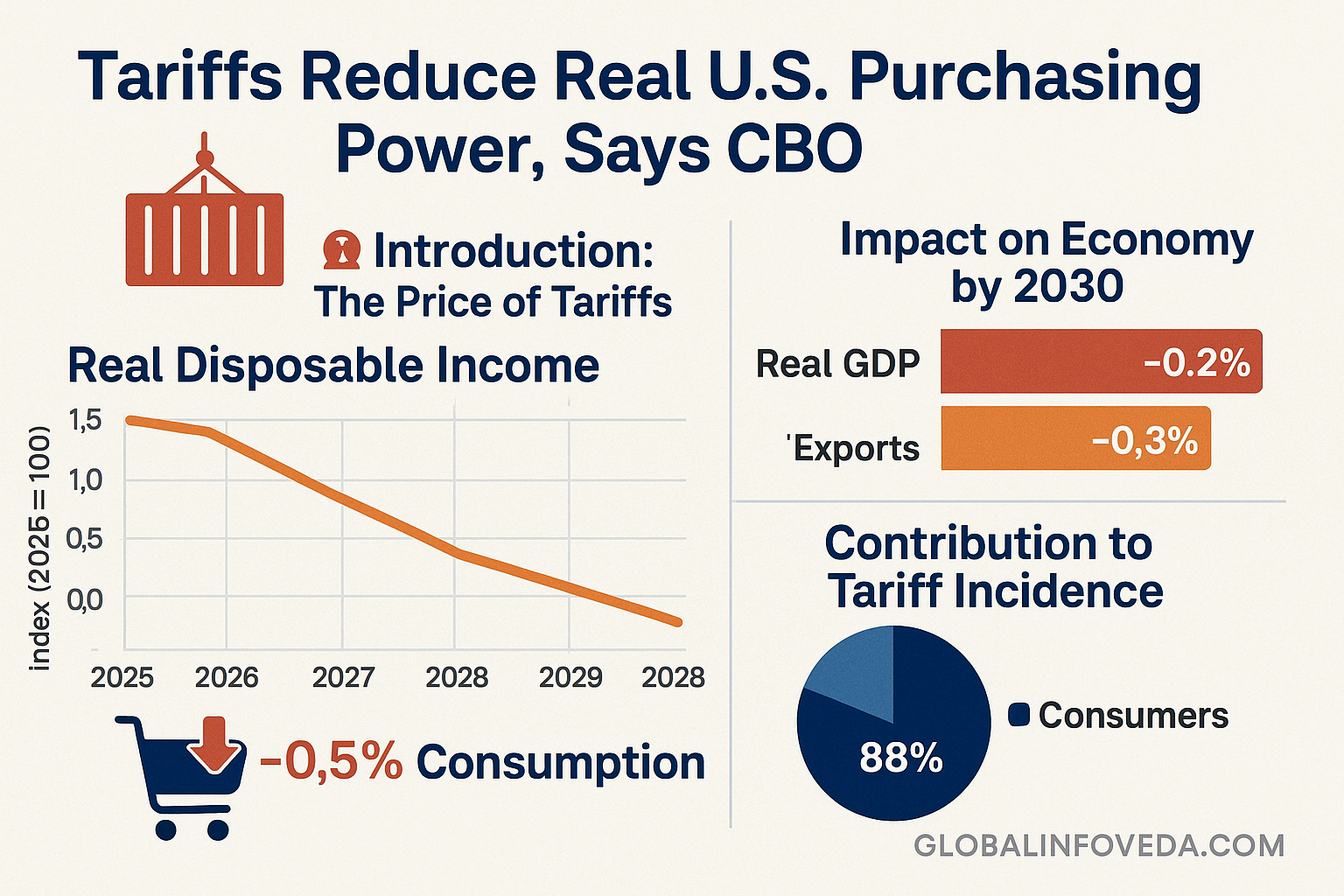
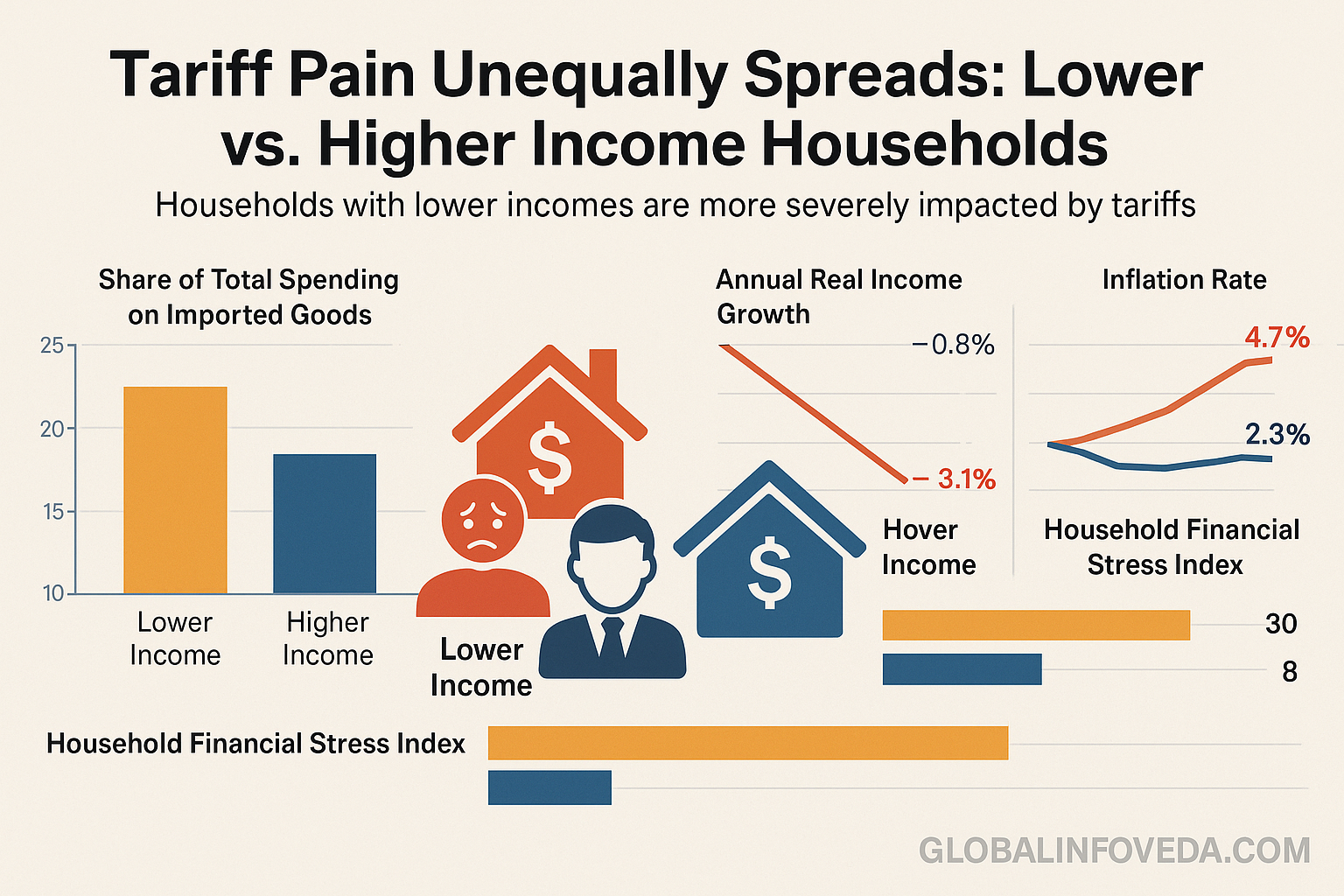
Macro view: Tariffs Reduce Real U.S. Purchasing Power, Says CBO
🧠 Finance and trade instruments to soften the blow
- 💳 Supplier credit insurance to guard against buyer defaults or cancellations.
- 🧾 Factoring for receivables tied to affected SKUs; mix banks and fintech platforms.
- 🛡️ Hedging discipline: Layer forward contracts monthly rather than timing the market.
- 🧑⚖️ Contract clauses: Insert tariff‑sharing and force majeure‑like language for policy shocks.
- 🚢 Incoterms shift**: For certain buyers, switching to FOB can transfer freight risk without losing the account.
🧠 What U.S. buyers are telling Indian suppliers (decoded)
- “Hold the price this quarter, we’ll adjust specs later.” → Protect the relationship; propose a limited‑time bridge price with a clear expiry.
- “We’re testing Vietnam/Mexico for comparison.” → Offer co‑manufacturing or finishing in a duty‑neutral hub to keep partial share.
- “Marketing can’t move MSRP.” → Counter with bundle packs, loyalty promos, or seasonal drops that maintain perceived value.
🧰 Supply‑chain housekeeping—small fixes that add up
- 🏷️ Barcode & carton redesign to shrink volumetric weight and cut ocean/air costs.
- ⏱️ Throughput mapping on factory floors to raise output 5–8% without capex.
- 🧯 Quality drift monitoring post cost cuts; avoid returns that nuke margins.
- 📦 Vendor‑managed inventory pilots for top buyers to smooth schedules.
🧮 Comparison — market re‑routing options for displaced volume
| 🌍 Region | ✅ What fits quickly | ⚠️ Watch‑outs |
|---|---|---|
| EU | Home textiles, apparel, chemicals with green specs | REACH compliance cost, energy volatility |
| GCC | Jewellery, seafood, homeware, fast fashion | Price sensitivity; FX linked to USD |
| ASEAN/Japan | Auto parts, functional fabrics, electronics adjacencies | Standards/quality bar; certification time |
🧪 Case story — MSME leather cluster avoids layoffs
A Kanpur leather MSME group faced U.S. cancellations on mid‑range bags. The cluster pooled design and sourcing, pivoted to EU with chrome‑free tanning, and used port‑near consolidation to load fuller boxes. In four months, unit costs were down 6%, shipments stabilized, and women finishers retained jobs.
🧠 Personal analysis: What the next 3–4 quarters likely look like
Expect a two‑phase pattern: a shock quarter with order gaps and cash strain, followed by a sorting quarter where surviving SKUs find new homes or specs. Firms that keep discipline on pricing, defend design‑in positions, and invest in process control will emerge leaner but stronger. Those that chase unprofitable volumes will face debt stress. The wildcard is policy: a partial thaw or carve‑outs for specific HS lines can change the calculus quickly, so exporters must stay ready to relaunch shelved SKUs within 30 days.
🧠 Frequently asked questions
🧾 Will U.S. buyers absorb any of the duty?
Some will—particularly for must‑carry lines with loyal customers. But in most price‑sensitive categories, buyers will push for shared pain: spec tweaks, bundle packs, or staggered promotions. Negotiating tariff‑sharing for bridge quarters can keep the account alive.
🧮 Does a weaker rupee solve the problem?
Not fully. A 2–5% depreciation helps but cannot offset a 25‑point tariff. Use FX gains for automation, quality, and new market entry, not as permanent discounts.
🧭 Which markets are quickest to enter as substitutes?
EU and GCC for apparel/homeware/jewellery; Japan/ASEAN for components and functional fabrics. Prepare for compliance and certifications.
🧑⚖️ What contracts should we update?
Add tariff‑sharing, policy‑shock triggers, currency bands, and Incoterms flexibility. Ensure dispute resolution and QC clauses are clear to avoid returns.
🛡️ What about insurance and credit?
Use trade credit insurance tied to your top 20 buyers. Mix bank and fintech factoring to smooth cash flow during renegotiations.
Context: Who Wins? How U.S. Tariffs May Backfire on American Consumers
🧭 Playbook for policymakers and industry bodies
- 🧭 HS‑line lobbying: Build a data‑rich case for carve‑outs on labor‑intensive lines that don’t threaten U.S. security priorities.
- 🧪 Quality & compliance grants: Tie support to process upgrades—dye house effluents, REACH documentation, traceability.
- 🧳 Market access missions: Fund multi‑cluster delegations to EU/Japan/GCC with pre‑booked buyer meets.
- 🧭 Digital trade: Push paperless customs corridors with partner countries to shave dwell time.
🧭 What large Indian buyers can do to steady MSMEs
- 🤝 Anchor orders: Place rolling POs with flexibility on specs to keep lines warm.
- 🧰 Shared services: Offer QA labs, design pods, and freight pooling to vendors.
- 💳 Faster payments: Early‑pay programs at discounted rates beat vendor distress.
🧠 The investor view—how portfolios can re‑balance
- 🧵 Watch export‑heavy mid‑caps in apparel, jewellery, chemicals for guidance cuts; look for efficiency pivots.
- 🦐 Aquaculture names face feed/cycle risks; monitor farmgate data.
- ⚙️ Auto ancillaries with diversified geographies and aftermarket share can be relative winners.
- 💵 Exporters with natural USD hedges and EU/GCC exposure are better placed.
🧠 Communications during turbulence—what not to say
- 🚫 Don’t promise “no price change” if you can’t hold it; reset expectations with spec change options.
- 🚫 Avoid blaming buyers publicly; protect long‑term trust.
- 🚫 Don’t cut QC corners to save pennies; returns kill credibility.
🧪 Case story — shrimp exporter saves farms via menu design
A Kakinada seafood processor seeing U.S. restaurant pain co‑designs smaller portion SKUs and weekday menus with chains that protect per‑ticket value. It also moves breaded and marinated packs to EU/GCC, keeping farmgate demand steady. Farm exits slow, and feed suppliers extend lines without defaults.
🧠 Media & narrative—tell the right story
India’s export story is not just low cost; it is reliability, compliance, and craft. Brands and trade bodies should push this narrative in global media while showing concrete steps on sustainability and worker welfare—the credibility wedge that keeps orders during storms.
📚 Sources (selected)
- Reserve Bank of India (RBI) — Bulletin & Market Developments: https://www.rbi.org.in/
- USTR — U.S.–India Trade Updates & Tariff Communications: https://ustr.gov/
- Reuters — Markets coverage on India and U.S. tariffs: https://www.reuters.com/
- Financial Times — India–U.S.–China trade dynamics: https://www.ft.com/
🌟 Final Insights
The 2025 U.S. tariff shock is painful, but not terminal. India’s strength lies in resilience, cluster depth, and the ability to re‑engineer product and process quickly. Firms that protect design‑in positions, shift from commodity to capability, and use data‑driven contracts will hold the line, even as they diversify to EU, GCC, and ASEAN. Policymakers can speed the transition with HS‑level diplomacy, skilling, and export finance that rewards quality. For buyers, retaining Indian partners now secures supply stability later. For workers, targeted support and re‑skilling can prevent scarring. The near‑term goal is not to win a trade war—it’s to keep markets, keep jobs, and keep moving up the value chain. 👉 Explore more insights at GlobalInfoVeda.com