📉 Introduction
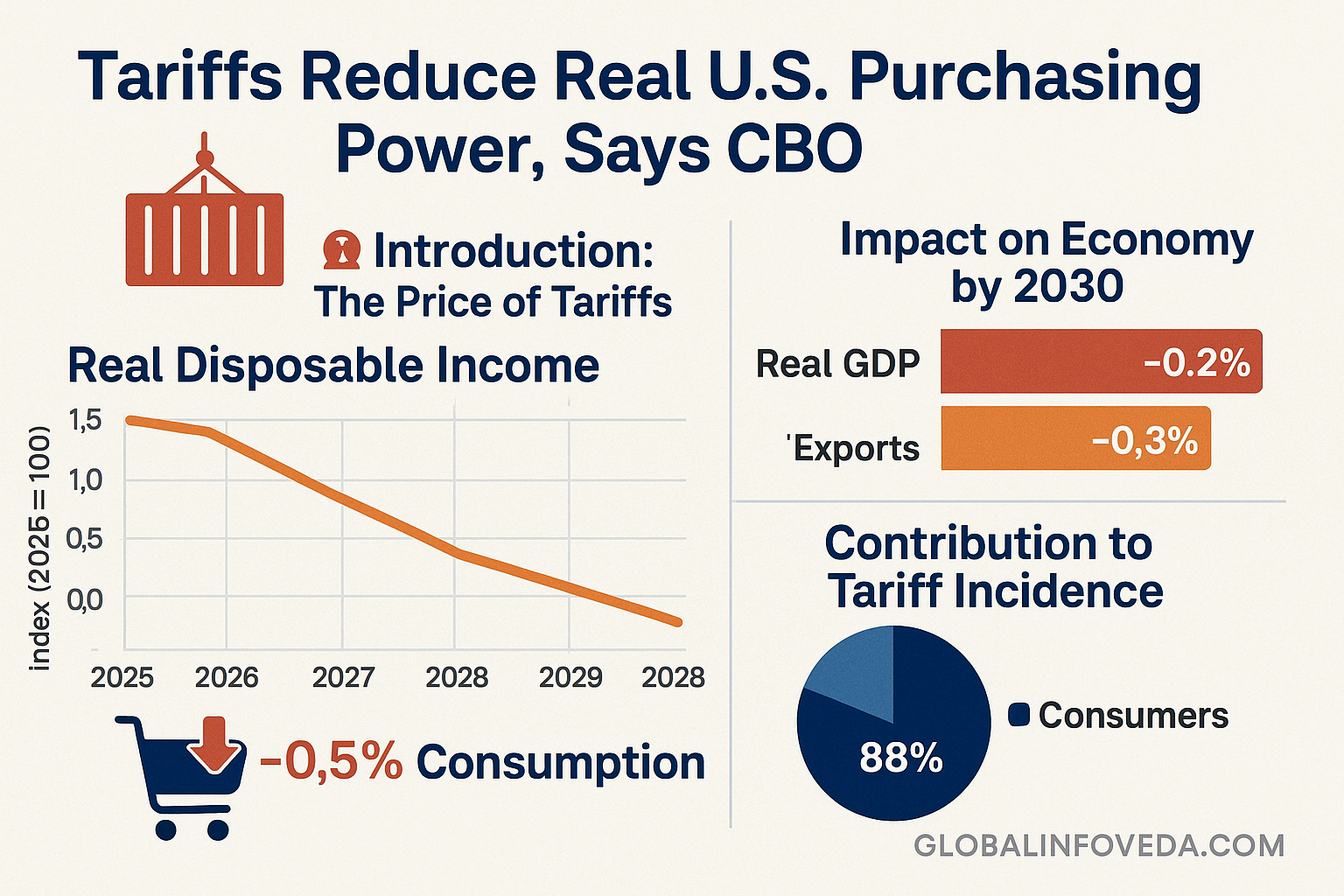
US GDP Wages: The 1st obvious Q in which US GDP y/y tumbles on the weight of monstrous tariffs came not as a single headline but via the accretion of momentum-squeezing frictions: pricier intermediate goods, longer port queues, margin-saving spec changes, and delayed capex that chipped away tenths of growth right until the sum turned negative. For households the story seemed simpler — wages didn’t stretch as far against higher consumer prices, the overtime disappeared in trade-exposed clusters and the second beer fridge or laptop purchase got postponed till next year. Businesses, meanwhile, were learning that every procurement work‑around levied its own tax: working‑ capital tied in bloated inventory, warranty buffers growing in step with spec tweaks, and sales teams needing to re‑anchor entry‑tier price points. This deep dive unpacks how tariff pressure went from micro to macro-forecasts in 2025, why the services side didn’t absorb all the blow, and what real-life playbooks will bring back bandwidth without sacrificing pricing honesty.
Meta description: U.S. GDP shrinks as tariffs bite: how wages, output, and services slow, plus playbooks for households, SMBs, and investors in 2025.
🧭 What a GDP contraction really signals
When BEA publishes a negative print, the discussion frequently defaults to whether the economy is already in technical recession. That framing obfuscates the operational interpretation of a shrink: the system’s throughput has encountered so much friction that output and the number of hours worked no longer scale with population and the capital stock. And in a year with tariffs, the mechanics are unusually concrete. A shipping crate that cleared customs in four days now needs documentation checks that cause it to sit for eight; the extra days are not just delay — they are carrying costs, insurance and lost shelf opportunity. A chip from a compliant hub is 7% more expensive, has a redefined heat tolerance profile and if the firm doesn’t change its spec card and warranty rules, return rates go up and the service centers are screwed up. Multiply those up by millions of SKUs and service lines, and you have a slowdown that isn’t so much about disappearing demand as frictional losses. The negative print is a macro ledger of these micro penalties. For families, it appears in thinner raises, delayed purchases and a hush-hush move toward refurb and repair instead of replace.
🧮 How tariffs travel from ports to paychecks
- 🧾 Landed‑cost step‑ups: Duties on inputs ripple through BOMs; firms that cannot pass through costs compress margins, trim shifts, or re‑scope products.
- 🧊 Port dwell and inspections: Extra days in queue tie up working capital; demurrage eats promotional budgets; more SKUs miss seasonal windows.
- 🧪 Specification tweaks: To hold the entry price, vendors modify materials or features; unless declared, warranty claims and reputational risk climb.
- 🔁 Dual‑sourcing overhead: Adding a second supplier reduces risk but raises audit and onboarding costs; wages feel it via constrained bonus pools.
- 🧱 Capex deferrals: Higher import bills crowd out automation projects; productivity growth stalls, setting the stage for weaker output per hour.
- 🧮 Pricing architecture drift: “Shrink by stealth” loses trust; transparent unit measures retain customers but require sharper procurement.
🧭 Data signals to watch beyond the headline print
The simplest trap in 2025 is to read the quarterly BEA line and mistaken the trend for destiny. The better trick triangulates: BLS payrolls and weekly hours in trade‑exposed clusters, ISM new orders in services that depend on imported disposables (outpatient, labs, salons), and port avail data to presage SKU avail. If inspection‑hold rates start to level out while warranty claims do not, that’s specs degradation not macro demand collapse. Similarly, if business surveys among small firms reveal steady intention to hire but poorer expected margins, the constraint is not order books but input cost. Keeping track of these supports sharper decisions: when to lock in freight, when to rotate menus in the direction of refill‑friendly packaging, when to issue fee calendars that maintain trust while costs equalize. In short, the smartest operators regard the GDP line the way baseball pitching coaches treat a radar gun tide as a lagging ledger and steer by the plumbing metrics that lead by weeks.
🧮 📊 Where growth went missing — components vs tariff sensitivity
| 🧩 GDP component | 🧲 Tariff exposure (stylized) | 🎯 Primary channel |
|---|---|---|
| Consumption (goods) | High in electronics, apparel, appliances | Landed cost → shelf price → unit volume |
| Investment (equipment) | Medium‑high in boards, machine tools | Import bills crowd out automation capex |
| Net exports | High via retaliation & compliance | Lower volumes, re‑routing costs |
🏭 Why the services cushion slipped in 2025
For a generation, slowing down in the United States was cushioned by the rise in services. The cushion began to wear in 2025 when many services, discreetly, relied on imported disposables, modules and packaging. A dental clinic’s cost base would include burs and sterilization pouches; a diagnostics lab would need reagents; a salon would use imported cartridges and refill packs; a logistics firm would be dependent on spare parts, tires and scanners. As these input costs increase with tardiness, appointment throughput stretches and fees float higher. The greater the tariff strain, the more fee schedules follow import quotes. This is not a cliff, it is a slope: the system is still functioning, but more slowly, and more expensively. The policy objective might be strategic, but the near-term arithmetic comes out of local businesses and wages until there is enough of a shift to new domestic capacity. That’s why headline jobs can stay positive while hours and real earnings decline — operators maintain employees to ensure service continuity but cut back on overtime and bonus pools in order to stay solvent.
🧰 A CFO’s teardown of margin math in a tariff quarter
A midmarket appliance maker demonstrates how the math penalizes indecision. Their landed cost increased 8% after rerouting boards through a compliant hub; freight premiums added 1.5%. Rather than publish a spec card and re‑anchor the entry‑tier feature set, the company pruned invisible contents, which increased return rates and undermined trust. Warranty expense was up 60 bps of revenue center staffing in service centers grew longer call times grounded customer experience scores. The sales staff retaliated with even deeper discounts that taught customers to wait for bargains. Gross margin was impaired twice: once by costs, again by promo addiction. The stock derated when the quarterly guidance finally fessed up to the mix shift toward lower‑margin SKUs. If so, the other alternative path — scope clarity, warranty transparency, and carton right‑sizing to drive container fill — would have been able to preserve share with less scuffing.
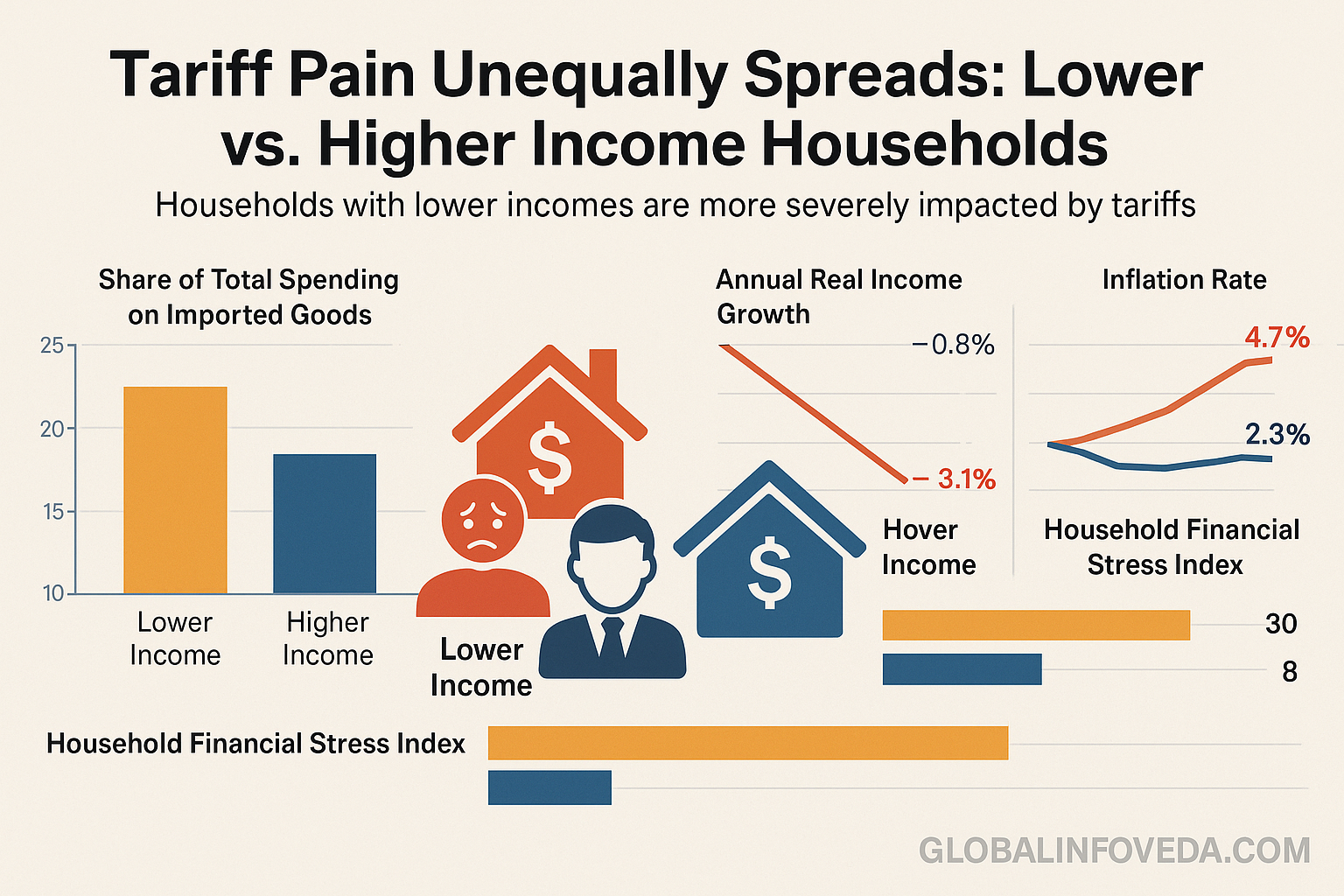
🧰 Households under pressure: where the paycheck leaks
- 🛒 Grocery basket: packaged staples and produce with longer cold‑chain legs absorb fuel and packaging surcharges; unit sizes shrink unless labels are policed.
- 🧴 Personal care: refill formats cut per‑use cost; bulk buys only win if consumption is disciplined—otherwise waste wipes the savings.
- 🧑⚕️ Healthcare payments: outpatient co‑pays creep higher as clinics pass on imported disposables; scheduling lead times lengthen.
- 📱 Devices: certified refurb with long OS‑update horizons beat mid‑cycle replacements; repair networks flourish.
- 🧰 Auto maintenance: tires, filters, and sensors carry premiums; a preventive 12‑week maintenance sprint saves the failure tax.
- 🧾 Debt service: higher card APRs plus larger grocery bills compress discretionary room; choose payoff ladders over scattershot extra payments.
Deeper dive on purchasing power: U.S. Families Could Pay $3,800 More a Year Due to Tariffs
🧪 Case study — two towns, same shock, different outcomes
- 🏭 Riverbend (manufacturing‑heavy): A tools plant faced component surcharges and inspection delays. Management froze hiring, cut overtime, and offered cross‑training to stabilize throughput. A local grocer pivoted to refill stations and regional produce to offset packaging costs. Result: wages flat to slightly down, but employment held; small businesses survived by redesigning offerings.
- 🏙️ Harborview (services‑leaning): Clinics and salons absorbed higher disposables pricing with modest fee hikes and longer appointment spacing. Logistics peers passed fuel surcharges using transparent tables. Result: income steadier but hours down; households leaned into repair, refurb, and community resale. The decisive variable was communication: firms that published fee calendars and specs retained trust; those that hid the ball bled customers.
🧮 📊 Exposure map — who feels tariffs first, second, third
| 🧷 Group | ⏱️ Hit timing | 🧭 Transmission |
|---|---|---|
| Import‑intensive SMEs | Immediate | Landed cost, freight, audits |
| Households | 1–2 quarters | Shelf prices, co‑pays, gas |
| Capital goods suppliers | 2–4 quarters | Deferred automation projects |
🧠 Labor market mechanics when growth turns negative
A shrinking U.S. G.D.P. does not by itself yield mass layoffs, especially in the sort of services‑dominant economy we fake capitalism and have (demographic tightness, et c. et c. — see my Plan ⁄ Pan demic headline post). Instead, employers cut overtime, delay the hiring of backfills, tighten shift swaps and trim contractor hours. The early signal is not the headline unemployment rate, but the average weekly hours line in BLS prints and the ratio of job openings to unemployed. In the context of a tariff in 2025, openings can stay high even as hours fall because firms will require staff to insure service continuity across slower running parts and packaging. Wage growth subsequently slows as the bonus pools contract, mix shifts to lower‑premium roles. For workers, the successful adaptation is skills adjacency: instead of doing a tariff-exposed job (import documentation), doing a resilience job (warranty audit, spec QA, carton optimization) that the employer has to finance in good times and bad.
🧰 Playbooks for SMB survival in tariff season
- 🧭 Publish scope: put spec cards on product pages and in stores; anchor the entry tier honestly and upsell with clear value, not mystery trims.
- 📦 Raise container fill: right‑size cartons; adopt nesting and multi‑SKU packs for high‑velocity items; track damage vs densification.
- 🔁 Dual‑source with discipline: one lead, one lag supplier; audit schedules staggered; golden samples stored locally for QA.
- 🧰 Repair and refurb lanes: monetize returns; partner with certified techs; warranty extensions that pay for themselves via retention.
- 🧾 Fee calendars: in services, publish quarterly price bands; customers forgive increases they can plan for.
- 🧮 Cash discipline: reserve against inspection‑hold volatility; negotiate freight blocks; demand shorter pay cycles from platforms.
🏦 Investment and financing under tariff strain
Negative growth quells animal spirits, but the underwriting weather is more nuanced. Large issues can roll commercial paper at fair spreads; the squeeze is more severe for mid‑caps that are import-dependent with slender disclosure. Asset-backed shelves are still available, but they reward granularity — clear warranty rules, low chargebacks, evidence of spec stability. Banks are more than liquid, even as term pricing rises, pushing borrowers towards shorter maturities and increasing their rollover risk. The antidote is transparency: companies that provide SKU‑level and route‑level metrics incur reduced funding costs because lenders can model risk. The paradox of 2025 is that storytelling becomes lighter and ledgers grow heavier; the kind of low-cost capital available only to operators who can actually prove their cartons, specs, and returns.
🧭 Monetary and fiscal mix when inflation is sticky
- 🏛️ Central bank stance: inflation that skews toward traded‑goods components leaves policy cautious; rate cuts wait for proof of disinflation that is not driven by demand destruction.
- 💸 Targeted relief: tariff‑rate quotas for high‑incidence medical disposables and safety equipment tamp secondary price pressure without altering strategy.
- 📊 Public dashboards: publishing port dwell, inspection‑hold rates, and green‑lane usage lets the private sector self‑correct congestion.
- 🏥 Standards fast‑track: pre‑clearing vendors with clean documentation shortens queues and stabilizes appointment throughput in services.
- 💼 Workforce skilling: grants for warranty techs, packaging engineers, and customs specialists align labor supply with resilience tasks.
🧠 Investor positioning through a contraction
Beta goes dull when U.S. GDP rolls over. Quality rules: high free‑cash‑flow yields, compressed reinvestment demands, and pristine working‑capital cycles. But quality is not one size fits all — some use transparent specs and carton math to keep margins; others guess and bleed returns. As investors pay for near‑dated protection, the options surface steepens, which favors put spreads and collars funded by call overwrites in names with distant catalysts. Duration assets rally if fear of growth outpaces fear of inflation; credit selection matters its a for tuition ish if import bills inflate working capital at the wrong time. Real assets cushion some shocks, but operators with brittle guarantees and opaque specs underperform even when the water level seems not to be falling. Where the slopes improve: Data is the edge With containers filled, rates of return and hold time (carry) — track them and be positioned where the slope improves.
🧮 📊 Three archetypes of firm behavior in tariff year
| 🧭 Archetype | 🧰 Hallmarks | 🎯 Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| The Fogger | Hides spec changes, random promos | Short‑term volume, long‑term churn |
| The Mechanic | Publishes specs, fixes cartons | Margin rebuild within 2–3 quarters |
| The Storyteller | Narratives without ledgers | Higher funding cost, valuation drag |
🧪 Case study — outpatient network that published the truth
One 22‑site network saw an 11% rise in disposables without predictable lead times. The CEO fought the across‑the‑board hikes, and instead constructed a fee calendar that was stacked with transparent tiers: off‑peak discounts, refill incentives, and a low‑income assistance lane funded through vendor rebates. Procurement, meanwhile, re‑engineered procedure packs to cut waste and secured tariff‑rate relief for particular SKUs. The network also released to patients a registry of device warranties and a standing specification library they could read. Wait times got better in eight weeks as no‑shows for appointments dropped (clarity of price diminished surprise) and clinicians spent less time unwrapping line items. Profitability recovered to pre-crisis levels by 2Q20 while preserving access.”
📦 Freight and packaging — where margin is found
- 🚢 Milk‑run routing: consolidating pickups across nearby suppliers reduces damage and chassis waits.
- 📏 Right‑size cartons: reduce void fill; use modular inserts; improve container fill by 6–12%.
- 🔁 Return‑to‑refurb loops: reclaim parts, extend warranties prudently; a managed refurb lane offsets new‑unit premiums.
- 🧪 Material swaps: where compliance allows, move to recycled resins and paperboards; cost stability improves as virgin inputs spike.
- 📊 Dock analytics: measure dwell, turn times, and damage rates; publish dashboards that operations can tune weekly.
🧠 Messaging that preserves trust under strain
Customers can swallow higher prices when they’re regarded as partners, not targets. The recipe is succinctness and truth in advertising: “Imported costs rose (by X); here’s how we’re protecting the entry‑tier value; here’s our warranty.” In services it is the same clarity: “Gloves and reagents are more expensive; we spread the impact with off‑peak discounts.” It can’t work for long because avoidography — the phenomenon of pages full of euphemism — works for a week and poisons the brand for a year. The social benefit of candor is reduced churn; the financial benefit is a lower cost of capital as markets reward predictability.
🧾 Household navigation — practical moves that compound
- 🧠 Plan big purchases around published promo windows; step off the panic treadmill.
- 🛠️ Preventive maintenance on cars and appliances; failure premiums are higher under tariff stress.
- 🧴 Refill and repair: prioritize products with published specs and parts availability; avoid sealed ecosystems.
- 📱 Stretch devices: certified refurb with long support beats new mid‑tier that risks early obsolescence.
- 💳 Debt ladders: concentrate extra payments to one balance; refinance only when fees don’t erase gains.
Consumer impact context: Who Wins? How U.S. Tariffs May Backfire on USA Consumers
🧭 30‑60‑90 day macro outlook
“In the next 30 days, the key factor will be if inspection‑hold rates at major ports of the U.S. stabilize and dwell reduces by at least a day — that opens up promotional calendars for retail and cuts back calendar days on emergency air‑freight (health and repair services). Looking out 60 days, prices will be in the lower left, watch ISM print services new orders and backlogs; if backlogs are falling without an order collapse, operators are clearing queues not losing demand. At 90 days, that second BEA forecast will have fresh inventory and trade data; if the contraction’s depth is revised milder, hours worked flattens, and we’re at the trough. None of this is heroic–just unglamorous labor on cartons, specs, and warranty queues. Policymakers can help by maintaining clarity on the calendar for tariff reviews so that procurement heads can plan without whiplash.
🌐 International spillovers and friend‑shoring reality
Neither does the big picture look like a neat one-for-one substitution, where imports seamlessly move from one source to another. Each new corridor requires audits, testing labs, warranty alignment. Friend‑shoring is a thing but lumpy; 1Q appears lower onboarding cost and lower container fill, not instant resilience. For the U.S., the way to capacity is through packaging engineers, customs experts, and QA techs—jobs that don’t trend much on social media but that determine vividly whether throughput can be resumed. For partners such as India, Southeast Asia and Mexico, the opportunity is medium‑term: vendors that can demonstrate compliance, publish spec cards and hit delivery windows will take durable contracts as buyers diversify risk.
🧠 My analysis: what would shorten the slump without abandoning goals
Three action steps would bring it about more rapidly, while having the support of strategic purpose. First, timeboxed TRQs on high-incidence medical and safety SKUs would restrain secondary inflation in services, without diluting the reshoring signal. Second, a national warranty transparency standard would remove the reward to conceal spec swaps, benefit consumers and responsible businesses equally. 3) green‑lane expansion linked to digitized origin documentation would both reduce inspection noise and also cut demurrage and restore retailer promo calendars. None of these alter the direction of the policy; they change its variance. Markets price variance as they do level—stability is the release.
❓ FAQs
- Does a negative GDP guarantee broader recession? No. A mild contraction can stabilize if inspection bottlenecks ease, fee calendars settle, and operators publish spec and warranty details that rebuild trust.
- Why do wages feel weaker even when jobs hold? Employers trim overtime and bonuses first; mix shifts to lower‑premium roles; real wages lag if traded‑goods inflation stays sticky.
- Are domestic substitutes always cheaper? Not initially. Onboarding costs and smaller scale raise unit costs; savings arrive after audits, carton redesigns, and volume learning.
- Should households accelerate purchases before more hikes? Only when specs and warranty are clear; panic buying locks in bad value.
📚 Sources
- Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) — national income and product accounts: https://www.bea.gov/
- Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) — employment, wages, and hours: https://www.bls.gov/
- Congressional Budget Office (CBO) — assessments of trade and macro impacts: https://www.cbo.gov/
- Federal Reserve (FRED/Board) — financial conditions and credit series: https://www.federalreserve.gov/
🌟 Final Insights
A quarter with U.S. G.D.P. in the red is not a verdict on the system’s resilience; it is the bill for friction incompetently navigated. The lever that closes the gap between wage rates and price of milk is not slogans flipping to subsidies; it is execution: honest spec cards, predictable warranty rules, carton math that increases container fill and green ‑lane logistics that turn days back into throughput. Households have their purchasing power protected by favoring refurb, repair, and refill ecosystems; SMBs can win now by tightening broadcast and tackling procurement; investors can sift through signal and noise by monitoring dwell, returns, and hours instead of the news. Do this consistently, and contraction becomes a brief detour on the way to stronger supply lines and better‑aligned incentives.
👉 Explore more insights at GlobalInfoVeda.com