🍲 Introduction
Consumers Tariff Adaptation: Across towns and suburbs in 2025, working families are adjusting to a life where they daily confront increases in the cost of living and sticky food inflation. This new normal is not a performance: smaller carts, more meal planning, and a clear pivot toward the $5 dinner, which feeds two or more persons, if the right combination of pantry staples, seasonal produce and kitchen discipline are wheeled into place. What seems on the surface to be thrift is in reality a deeper design problem — stretching wages, cutting waste, and defending nutrition while rent, fuel and service fees run hotter than paychecks. This guide maps the new landscape: how the math of grocery shopping changed, if households are making adjustments and what low-cost meals can still deliver protein and fiber and which attitudes preserve dignity and good health without burning your last smidgen of time or energy.
Meta description: How working families survive food inflation in 2025—smart $5 dinners, grocery math, nutrition trade‑offs, and dignity‑first strategies that really work.
🧭 The new household economics behind $5 dinners
The march toward $5 dinners isn’t meme‑driven; it’s ledger‑driven. And they are reconciling a series of weekly pay cycles with bills that reset faster than salaries do —so the grocery line item is the balancing valve. The point isn’t to skip quality, but to skip resistance: impulse buys, specialty packaging, and unrecoverable leftovers. By paring down menus to a handful of base starches (rice, potatoes, rotis, pasta), rotating budget proteins (eggs, lentils, chickpeas, canned fish, paneer or tofu on sale) and anchoring flavors around long-lasting aromatics (onions, garlic, chilies), households re‑create restaurant comfort in compact, repeatable shapes. The method relies on batch prep for sauces and spice mixes, a freezer-staging area for pre-cooked beans or bhuna bases, and a marked “use-first” bin that prevents produce from disappearing to the back of the fridge and being wasted. When it goes right, the result is not of food scarcity but food predictability — a rhythm that shields nutrition and cash flow alike.
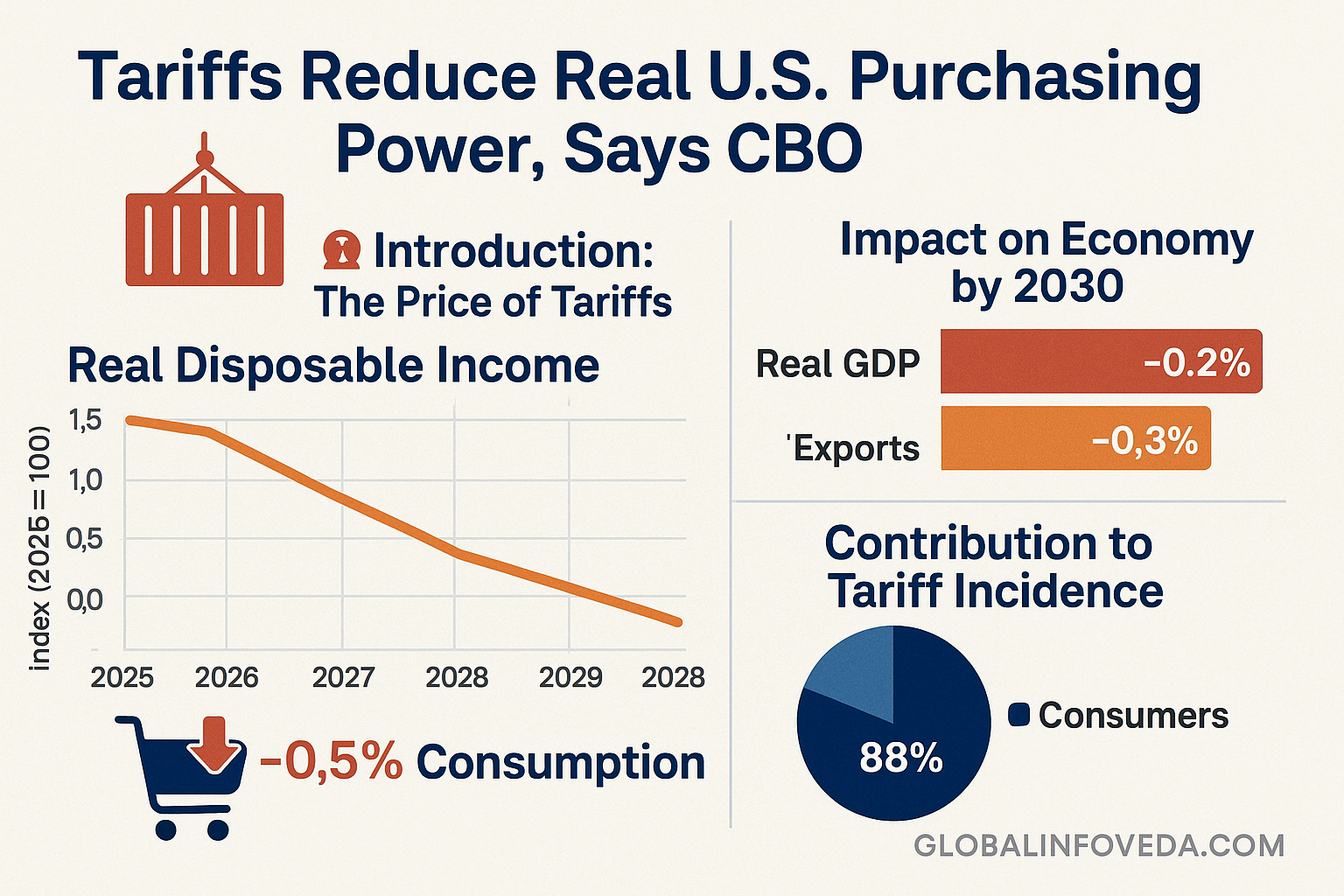
Explore related household cost impacts: U.S. Families Could Pay $3,800 More a Year Due to Tariffs
🧪 Why budgets broke: the three‑line squeeze
- 💸 Food inflation outpacing wage growth: even small monthly increases compound; unit sizes shrink while sticker prices hold steady.
- 🚚 Freight and packaging pass‑through: diesel and cold‑chain surcharges roll into dairy, produce, and frozen aisles; specialty packs raise per‑portion cost.
- 🏠 Rent and utilities crowd out groceries: landlords price to market while electricity and gas track global inputs; the grocery line absorbs the shock because it is the most flexible.
🥣 What a good $5 dinner really means in 2025
Today’s $5 dinner is not an individual item. It is a plate composition — a satiating balance of protein, fiber, flavor and cost — that finds the lowest common denominator, and triumphs. I’m talking one budget starch, one robust vegetable and one versatile protein mixed up with a punchy base (gentle spices, soffritto or a peanut‑chili emulsion). The power move is to make a batch of flavor base once and re‑use it in three ways over the course of the week — stir‑in for stews, thin‑out for broths, spread‑on for wraps. Seasonality counts: The backbone at those price spikes are cabbage, carrots, onions, and potatoes; quick‑cooking greens, pumpkin, and plantains rotate in where the local markets peg them low. Meaning: predictable satiety without relinquishing freshness, accomplished by relying on citrus, pickles and chilies to elevate plain staples.
📊 🧮 $5 dinner pathways: cost vs time vs nutrition
| 🍽️ Plate design | ⏱️ Time to table | 🧠 Nutrition focus |
|---|---|---|
| One‑pot lentil + rice + veg | 25–30 min | Protein + fiber + potassium |
| Egg bhurji wraps with slaw | 15–20 min | Protein + B‑vitamins |
| Chickpea pasta arrabbiata | 20–25 min | Protein + slow carbs |
🧰 Pantry architecture that lowers monthly spend
- 🫘 Protein bins: dry dal, chickpeas, and soya chunks; rotate with eggs and canned fish for variety and shelf stability.
- 🌾 Base starch stack: rice (short and long grain), poha, whole‑wheat flour, potatoes; pick two per week to avoid half‑used bags.
- 🧅 Flavor cores: onion‑garlic‑chili triad, tomato paste, tamarind or lemon, one dark soy or jaggery; small bottles prevent waste.
- 🧂 Spice sets: one garam blend, one chili, one cumin‑coriander; add mustard seeds and curry leaves if South Indian flavors anchor comfort.
- 🧊 Freezer lanes: pre‑cooked beans in flat packs, blanched greens, bhuna masala cubes; flat packs thaw faster and cut emergency takeout.
- 🧴 Fats: one neutral oil + one flavor oil (sesame/mustard); stick to two to control per‑ml costs.
🥗 Seven $5 dinner templates families actually repeat
- 🍛 Masoor khichdi + cabbage kachumber: pressure‑cooked red lentils and rice tempered with cumin, turmeric, and garlic; raw cabbage‑onion salad with lemon and salt for crunch.
- 🌯 Egg bhurji roti rolls: spiced scrambled eggs with onions, chilies, and tomatoes rolled in fresh rotis; yogurt dip with dill or mint.
- 🥘 Potato‑pea curry + rice: tempered mustard seeds, garlic, and chilies; simmered potatoes and frozen peas; finish with lemon and coriander.
- 🍝 Chickpea pasta arrabbiata: a quick onion‑garlic‑chili base stretched with tomato paste; toss with chickpea pasta for extra protein.
- 🥔 Aloo tikki burger bowls: pan‑seared potato patties, shredded carrots, cucumber, and a spicy yogurt; toasted stale buns as croutons.
- 🥬 Cabbage‑egg stir fry + steamed rice: high‑heat shredded cabbage, eggs, soy splash, and vinegar; chile oil optional.
- 🐟 Canned tuna pulao: quick pilaf with onions, chilies, canned fish, and peas; lemon‑pickle on the side.
🧠 Nutrition guardrails that don’t cost extra
A grocery bill shrinks fastest when protein is protected and fiber stays high—satiety follows and snack spend falls. The mistake most families make is cutting produce first and then chasing fullness with packaged treats that cost more per calorie and less per micronutrient. A better rule is to keep one dark green (spinach or mustard leaves), one orange (pumpkin or carrot), and one crucifer (cabbage or cauliflower) across the week, even if portions are small. For working families, a tablespoon of seeds (sesame, flax, sunflower) stirred into doughs, salads, or porridge quietly raises mineral intake. Finally, water first: cold water or lemon water before meals helps curb reflex snacking without touching the budget.
🧮 📊 Value cooking vs convenience buys vs takeout
| 🛒 Option | 💵 Typical cost per plate | 🎯 When it wins |
|---|---|---|
| Cook at home (value) | ₹100–₹200 / $1.2–$2.5 | Maximum control, leftovers, nutrition |
| Convenience kit | ₹200–₹350 / $2.5–$4.5 | Crisis nights, predictable portioning |
| Takeout special | ₹300–₹500 / $4–$6.5 | Only if shared or next‑day lunch guaranteed |
🧭 Grocery route maps that stop waste
One of the most significant cost leaks isn’t so much the sticker price as the waste tax — greens that soften before they’re used, buns that go stale before you can use them, sauces that turn. Route design fixes this. Families go on one “heavy” trip for shelf goods and bulk starches at a value store, and then two quick produce runs at neighborhood markets to get what they actually need. The cart begins with the plan: one foundational starch for weeknights, one for weekends; two proteins to alternate so that boredom doesn’t inspire takeout; and three vegetables that may be cross‑used across dishes. With it, food waste becomes less likely, the late-night order less so. Having a “eat‑first” box always in view, as a running catalog, provides yet another guardrail: Whatever’s in there has to be cooked next, period.
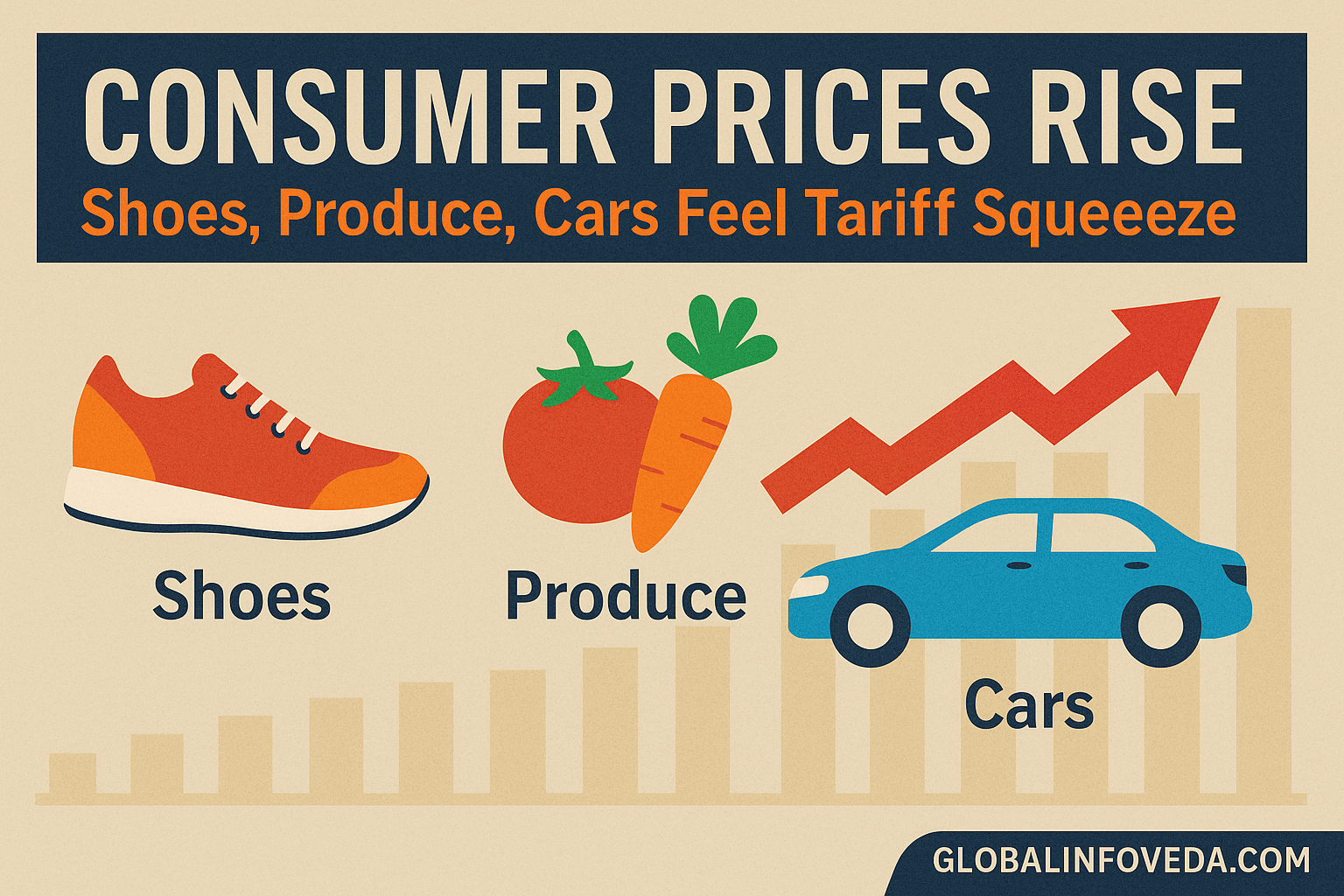
Price pressure context: Consumer Prices Rise: Shoes, Produce, Cars Feel Tariff Squeeze
🧰 Kitchen time math for two‑job households
- ⏱️ 25‑minute floor: plan around one‑pot dinners that never exceed half an hour on weeknights; save layered curries and bakes for Sundays.
- 🧊 Freeze in flats: cooked beans, dal, sauces in zip‑flat packs; stack like books; thaw fast under tap.
- 🔁 Three‑use base: one masala or soffritto used for stew, soup, and wrap filling across three nights.
- 🥄 Pre‑measure spices in film canisters or tiny jars; label 1–2–3 for steps; remove decision fatigue at 7 pm.
- 🧽 Sink discipline: fill, soak, and reset during simmer; a clean sink stops the “let’s order” impulse.
🧠 Mental health under money strain
Food insecurity can spiral rapidly in working families — especially when children notice the absence of their favorite dish or parents forgo extra portions. The antidote is visible plenty that can be conjured with cheap tricks: big bowls of roast potatoes or chana, bright slaws, sliced fruit with chaat masala, and unlimited water, or nimbu pani. Have teens participate in budget cooking competitions; gamify “pantry clears” as a point of pride, not a punishment. If social media is heightening your comparison stress, mute it and spend time in group chats where you swap actual recipes and local sale alerts. Homey anchors like a Friday movie with freshly made popcorn that costs pennies and announce that joy remains on the calendar.
Further well‑being context: Wellness 2025: Trends to Skip—and What to Try Instead
🛠️ School‑night $5 menus kids actually eat
- 🧡 Tomato‑egg drop soup + toast sticks: quick broth with tomatoes, garlic, beaten eggs; toast stale bread brushed with oil.
- 💚 Peas pulao + carrot raita: fragrant rice with frozen peas; yogurt with grated carrot and cumin.
- 💛 Cheesy aloo quesadillas: mashed spiced potatoes between rotis or tortillas; crisp on tawa; salsa from chopped onions and tomatoes.
- 💙 Masala oats upma: rolled oats, mustard seeds, chilies, onions, and frozen veggies; finish with lemon.
- 🧡 Moong chilla wraps: blended moong batter pancakes with slaw and chutney; protein‑dense and fun to roll.
🧑⚕️ The health case for $5 dinners
Cheap food is frequently lampooned as unhealthy, but $5 dinners can be high in protein and fiber if they’re anchored by lentils, eggs, leafy greens or whole grains. The real damage comes from so-called cheap ultra-processed snacks that feel like they are saving us money but don’t provide any fullness, making us eat more. A pot of masoor dal with spinach and garlic over rice provides iron and folate at a fraction of what those processed bars cost. A cabbage‑egg stir fry brings choline and vitamin K to the table in no time. A potato‑pea curry gets its vitamin C from lemon juice squeezed over at the end, which, incidentally, helps iron absorption. It’s the pattern more than the single meal: simple repasts repeated beat out scattered “health hacks.”
📊 🧮 Pantry staples showdown: price, prep, versatility
| 🧺 Staple | 💵 Budget stretch | 🧑🍳 Versatility |
|---|---|---|
| Red lentils (masoor) | Excellent | Soups, curries, patties |
| Eggs | Strong | Scrambles, wraps, stir‑fries |
| Cabbage | Excellent | Slaws, sautés, fillings |
🧾 How to read a shelf label like a pro
- 🔍 Unit pricing: ignore the giant font; scan the per‑100g or per‑kg number; branded value packs are sometimes pricier per gram.
- 📦 Spec changes: look for shrinking weights or lower‑quality oils; compare last month’s label photos if possible.
- 🧪 Additives: shorter ingredient lists usually mean higher cooking control; decide where convenience is worth the trade.
- 🧃 Juice vs whole: choose whole fruit where possible; fiber controls glucose and hunger.
- 🥛 Dairy choices: yogurt in tubs beats single‑serve cups on price; learn to set curd at home when milk is discounted.
🧭 Community hacks that multiply savings
There are more savings in neighborhood networks than any app offering coupons. Tool libraries for pressure cookers or food processors, WhatsApp groups to alert late‑night bakery clearance sales and weekend neighbourhood meet-ups with kids lunchbox ideas all alleviate stress with food. Joint bulk buys of basics reduce per‑unit costs; co‑pasta-bake-making sessions result in two weeks of freezer meals in the cooking time of one. A basic “who is cooking what” Google Sheet shifts boredom to pleasant anticipation, and overlap falls away. In apartment buildings, a rotis‑only or idli‑only rotation among three flats assures variety and a daily minimum of manual labor. Dignity rises as shared effort does.
🧰 The dignity play: language that protects morale
Words shape kitchens. Describe them as light nights balanced by hearty lunches (instead of “skipping meals”); refer to leftovers as planned overs and, rather than “cheap,” say smart or savvy. Children absorb money talk; telling them they are on a team safeguards their pride. Publicly celebrate wins — “Five home‑cooked nights achieved” or “We cut waste in half this week” — and make treats earned milestones, not guilt‑ridden indulgences. A family notes app can keep track of new recipes and prices, turning thriftiness into a friendly contest. It adds up to savings over months, more than any one discount, because it sustains the energy to keep cooking.
🧪 Case study — two incomes, two kids, one steady plan
A nurse and a warehouse coordinator who have two school‑aged children were hit with a rent increase that eliminated their meager surplus. They transitioned to a “three‑base” meal plan: rice, rotis and potatoes constituting the weekly backbone; eggs and lentils serving as rotating proteins; cabbage, carrots and onions as the underpinnings of vegetables. They would make a good portion of a tomato‑onion masala on Sundays, freeze it in two‑cup packets, and use it as the base for dal, pulao and wraps. One visible “eat‑first” bin alone reduced waste by 70%. He replaced chips with roasted chana and popcorn. The savings paid for one takeout night a month and a kids’ outing every quarter. The when and the how are not yet clear, but 12 weeks in, their food spend was down 18%, their general nutrition had held up, and their stress level was lower.
🧠 My analysis: where policy meets pantry
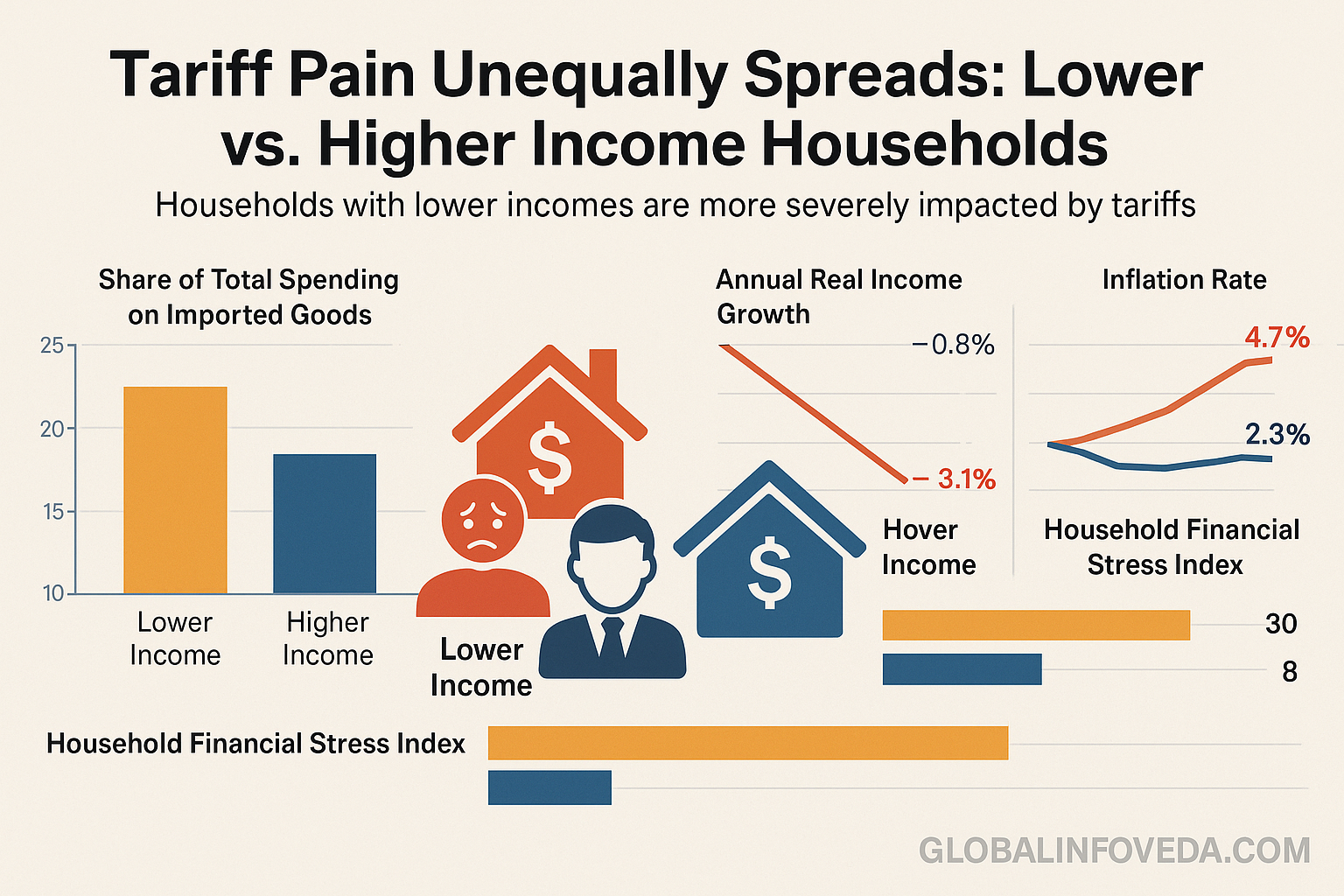
There’s a tendency to talk about food inflation as if it were the weather — something that takes place to families. In fact, it’s the intersection of policy, logistics and retail practice. When tariffs drive up input costs, and fuel surcharges whack cold chains, shelves empty and prices drift higher. But the distance between sticker price and dinner plate remains bridgeable when supply chains publish spec changes, retailers police unit pricing and municipalities encourage community markets and co‑ops. The best solution is transparency: It puts a halt to stealth shrink and gives families the information advantage. Here, targeted nutrition programs, focusing on beans and eggs as well as on veg in season, are better for working families than blanket subsidies for ultra‑processed goods.
🧰 Shopping route examples for different neighborhoods
- 🏬 Big‑box + local market: monthly bulk rice, dal, oil; twice‑weekly greens at the wet market; bakery clearance after 8 pm.
- 🛵 Transit corridor: small carts every other day near bus stops; carry a foldable tote; buy only what fits.
- 🏘️ Suburban ring: weekly farmers’ market for in‑season deals; discount grocer for tins; neighbor share for Costco‑size packs.
- 🏙️ Dense urban: leverage corner stores for onions, potatoes, eggs; frozen veg from larger chains; partner with a neighbor for shared freezer.
🥬 Plant‑centric plates that cost less and fill more
- 🌿 Chana‑palak stew over rice with lemon; leftovers thicken into wrap filling.
- 🥕 Carrot‑moong dal with cumin and garlic; pairs with poha upma for texture contrast.
- 🥔 Aloo‑gobi with peas and pickle; crumbled paneer is optional when on sale.
- 🌶️ Rajma bowl with cabbage slaw and a yogurt‑tamarind drizzle.
🧑🏽🍳 Flavor tricks that make budget cooking exciting
- 🔥 Tadka timing: bloom whole spices in hot oil; add aromatics; then liquids; tiny amounts transform simple starches.
- 🍋 Acid at the end: lemon, tamarind, or vinegar brightens and reduces salt needs.
- 🌶️ Controlled heat: a teaspoon of chile crisp on the table lets adults scale spice while kids keep it mild.
- 🧄 Roasted garlic: batch roast and freeze in oil; smash into potatoes, dal, or toast.
- 🧅 Pickled onions: quick pickle with salt, sugar, and vinegar; keeps a week; lifts bowls for pennies.
🧾 Stretch‑friendly breakfast and lunch rotations
- 🌾 Poha with peanuts + fruit; fills fast, reheats well.
- 🫘 Leftover dal as sambar‑ish soup with added veg.
- 🥪 Aloo masala toasties from last night’s potatoes.
- 🥣 Oats porridge with jaggery and seeds; stir in grated apple.
- 🥗 Chickpea salad with cabbage, carrot, onion, lemon, and a spoon of curd.
🧠 Children’s nutrition without budget blowouts
Children should get their protein, fat, and micronutrients, not cartoon graphics. Two eggs, a cup of dal or a palm of chana supplies a large chunk of your daily protein requirement at relatively low expense. Full‑fat yogurt stabilizes appetite. Fruit for dessert — bananas, oranges, seasonal guavas — beats bars and pouches on cost, and on fiber. Packed in bento-style lunchboxes, small quantities look abundant: a few cucumber slices, a boiled egg, a roti roll, a tiny sweet, de-weaponize snack envy. Get kids to help, whether it’s rinsing dal, spinning salad or pressing rotis; when they help, they eat better.
🧪 Case study — single‑parent resilience
A 6-year-old daughter of a delivery driver with night shifts, he slept in chunks. It was cooking energy that had been the true constraint. The answer was a two-hour block on Sunday that yielded masoor dal, aloo-matar, boiled eggs and a cabbage slaw base. Rotis were par‑cooked and stacked; portions were boxed in the freezer in flat packs. Only for few reheats and quick tadkas were called for on weeknights. On Friday, the routine was movie night, with popcorn and sliced fruit. Monthly food costs dropped 22 percent, takeout almost entirely vanished, and the child’s lunchbox became less humdrum as components cooked up and mixed and matched easily. The parent felt less guilt, and more control — evidence that time design is not only as important as money, but may be more important.
🧠 When skipping meals is a warning light
An “easy night” is acceptable on occasion; ongoing meal skipping that leaves adults irritable and kids sluggish is not. Warning signals: dizziness, inability to concentrate in school, headache and nightly snacking binge that cost way more than it would to just have a nice rice‑dal dinner. The fix is there in routine: Set mealtimes and a fallback soup or khichdi that is always an option: protein bolted in at lunch, if dinner could run to thin. Low‑drama requests work best, so if you can ask early, well in advance, that’s better than after a disaster strikes. Pride matters; so too does stability.
🧰 Small appliances that truly earn their keep
- 🔪 Pressure cooker/Instant Pot: the single biggest fuel and time saver for beans and dals.
- 🍳 Cast‑iron or heavy skillet: sears, roasts, and lasts decades; needs only oil and heat.
- 🧊 Freezer‑safe boxes and zip‑flats: convert weekend work into weeknight ease.
- 🥣 Stick blender: blitz soups and sauces; kids eat more veg.
- 🧂 Digital scale: stops over‑portioning; savings accrue quietly.
🧭 Regional twists on $5 dinners
- 🧡 South: tomato rasam with rice; curd rice with pickle; cabbage poriyal.
- 💚 North: chole‑chawal; aloo‑palak; moong dal tadka with jeera rice.
- 💙 West: zunka with bhakri; usal‑pav; masala poha with peanuts.
- 💛 East: alu posto; cholar dal with rice; egg curry with mustard.
- ❤️ Global: lentil bolognese; shakshuka; potato‑leek soup; tuna‑rice bowls.
🧠 Label honesty and consumer rights
Stores and brands could come to the party: clear unit pricing, honest sizes, and a listing of spec and recipe changes. One of the quickest ways to rebuild the trust is the publish a “what changed and why” when you reformulate product, or if you’re shrinking packs. For new counters, a uniform scoop size and posted weights are there to align expectations. Municipalities can mandate that perish‑by dates and discount windows be transparently posted; when households are informed on the timing, they plan. Enforcement is less expensive than crisis aid because it decreases the likelihood of fraud and waste before money leaves wallets.
🧾 Fuel and transport leak fixes
Commuting to cheaper stores can erase savings; the trick is to batch errands and assign routes. Ride‑share costs collapse when three families synchronize heavy shops once a month. Bicycle panniers or foldable trolleys expand carrying capacity without fuel. Freezer sharing in apartment blocks prevents “I can’t buy bulk” defeats. If public transport is reliable, piggyback the big shop on trips already being taken for school or clinic visits. The fuel line shrinks without touching the kitchen.
🧰 The endgame: stability, not austerity
A sensible food routine for working families is boring in the best way: a few beloved recipes on rotation, pantry discipline that clears mental and emotional space for kids and work, small pleasures guarded like line items. The goal is not to outperform other people at an online game but to create a household operating system that can take a blow — an unexpected bill or sickness, a spike in consumer prices — and stay standing. Once that operating system is in place, what was saved at the grocery is then money for paying down debt, emergency funds or even a little joy for the odd occasion. That’s how $5 dinners go from a tactic in an emergency to a strategy.
❓ FAQs
- Can $5 dinners meet daily protein needs? Yes, with eggs, dal, chickpeas, or canned fish as anchors; pair with greens and a starch for completeness.
- Is bulk buying always cheaper? Only if storage and consumption are planned; otherwise spoilage cancels discounts.
- How do we avoid palate fatigue? Rotate sauces and aromatics; keep the same structure but swap flavors—garam one night, soy‑ginger the next, lemon‑herb later.
- What if cooking energy is the constraint? Batch once weekly, freeze in flats, and rely on one‑pan meals that reheat well.
📚 Sources
- United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) — food budgets and MyPlate: https://www.usda.gov/
- World Health Organization (WHO) — diet and nutrition basics: https://www.who.int/
- Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) — consumer price indexes: https://www.bls.gov/
- Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) — food price trends: https://www.fao.org/
🌟 Final Insights
Families hacking through food inflation in 2025 aren’t chasing improvements; they’re building repeatable systems: tight pantry architecture, honest spec awareness, and simple $5 dinners that maintain nutrition and free up cash for stability goals. The victories are cumulative — less waste, more stable energy, quieter evenings, children who eat what is made (having helped select it). When a community can share tools, routes and recipes, the burden is lifted and the dignity uplifted. The answer is the one that your household can execute in tired weeks: one‑pot dal and rice, eggs with slaw, potato‑pea curry, a bowl of fruit. Consistency trumps novelty — and over a couple of months that consistency both rebuilds savings and morale.
👉 Explore more insights at GlobalInfoVeda.com