🚀 Introduction
When the “Liberation Day” tariffs were announced on the morning of Aug. 23, 2018, the message was supposed to be about strength. Running stops instead of getting back on the bull, all that did was cause a coordinated risk reset move that went from stocks, to credit spreads, to FX, to commodities and led to the most abrupt stock market crash the year 2025 came bearing witness to. Traders who had sketched a narrow, targeted programme were confronted with a sweeping plan that featured retroactive enforcement windows, strict rules‑of‑origin and proud proclamations of the interruption that will always be available. The effect was a frenzy to reprice earnings, a liquidation of crowded plays in cyclicals, and a mad dash into cash that caused even defensive service names to totter. Underneath the screens, the real story was gentler but just as consequential: logistics detours, input squeezes and policy uncertainty tightened the screws on operating cash flows and household consumer prices. This deep dive provides insight into how the shockwave reverberated, who suffered most from the impact, and how operators and investors can plausibly adjust 30–90 days out.
Meta description: The “Liberation Day” tariffs jolted global markets—unpacking the stock market crash 2025, earnings math, sector impact, and practical playbooks.
🧭 What exactly happened on “Liberation Day”?
The policy package bundled headline tariff rates with technical details that were far more significant than podium percentages. First, a number of categories were retroactively valued, requiring importers to hold on to cash for possible adjustments and penalties. Second, strict rules‑of‑origin further pushed exposure beyond a single country, which swept up multi‑node supply chains supplying U.S. shelves. Third, the signaling effect — the clear implication that the rate review would be quarterly — increased the likelihood of sustained tariff pressure. Market makers widened spreads, risk desks shrank balance sheets, and index sellers crushed buyers for hours. The stock market crash 2025 story is not just about fear; it is about pipes: the collateral demands, then the prime‑broker VaR breaches and basis blowouts, that mechanically forced trades to close. By the time the closing bell rang, implied volatility had doubled compared with the previous week, and cross‑asset correlations were racing toward one.
🗓️ Timeline: the first 10 trading days and the hidden gears
Equity markets gapped lower in the opening session, with the tariff‑sensitive baskets—apparel, consumer electronics, tools, and auto components—experiencing the largest losses. Day two brought a partial mean reversion as dip buyers tested supports, but credit spreads wouldn’t tighten, telling this was more than a squall. Days three to five were marked by re‑rating across defensives and hospitals, brokers, and utility names outperformed, but the respite was thin; forward services inflation assumptions edged higher as providers published fee‑revision calendars. By the end of day seven, options desks noted relentless put demand at skewed strikes, more consistent with institutional hedging than retail panic. On day eight, there were whispers of circuit breakers on smaller exchanges after liquidity in mid‑caps thinned, and ETFs in niche sectors traded at discounts to net asset value that were at odds with their past performance. Days nine and ten set in over a choppy rectangle with lower highs — classic damage repair — while desk chatter began to go from “how deep” to “how long.”
🧮 📊 Cross‑asset pulse (day‑10 snapshot)
| 🧭 Asset / Macro | 🔁 Direction move | 🎯 Market read |
|---|---|---|
| Equities (broad) | Down 12–18% from pre‑announcement | Earnings drag + de‑risking |
| Investment‑grade spreads | +40–80 bps | Balance‑sheet caution, funding dearer |
| Oil / copper complex | Mixed to down | Growth scare vs supply path |
🧠 How tariffs become earnings downgrades
- 🔄 Pass‑through friction: If landed cost rises 5–12% but cannot be passed on due to competitive anchors, margins compress immediately in mass‑market retail, quick‑service dining, personal care, and outpatient services.
- 🧰 Capex deferrals: Imported boards, alloys, and spares become dearer; maintenance turns into patchwork; productivity projects slip, taking next‑year earnings per share lower.
- 📦 Inventory timing: Port dwell adds working‑capital drag; carrying charges creep up as credit lines reprice.
- 🧪 Spec changes: Vendors reformulate to meet cost targets; warranty reserves rise; brand equity takes collateral damage.
- 🧮 FX wildcards: Currency swings can buffer or amplify the duty math, complicating guidance for CFOs.
🧩 Who sold, who bought, and why liquidity thinned
- 🏦 Balance‑sheet providers trimmed inventory risk as VaR jumped, forcing wider bid‑ask spreads and lower size.
- 🧾 Risk‑parity and vol‑control funds reduced gross exposure mechanically as realized volatility spiked.
- 👛 Retail reduced discretionary cyclicals via passive flows; 401(k) autopilots damped the move but could not reverse it.
- 🛡️ Long‑only managers rotated into cash‑rich defensives and services with pricing power, then waited.
- 🧮 Macro funds bought duration on growth scare, sold beta, and hunted for basis mispricings.
🏗️ Sector lenses: where tariff pressure bites first
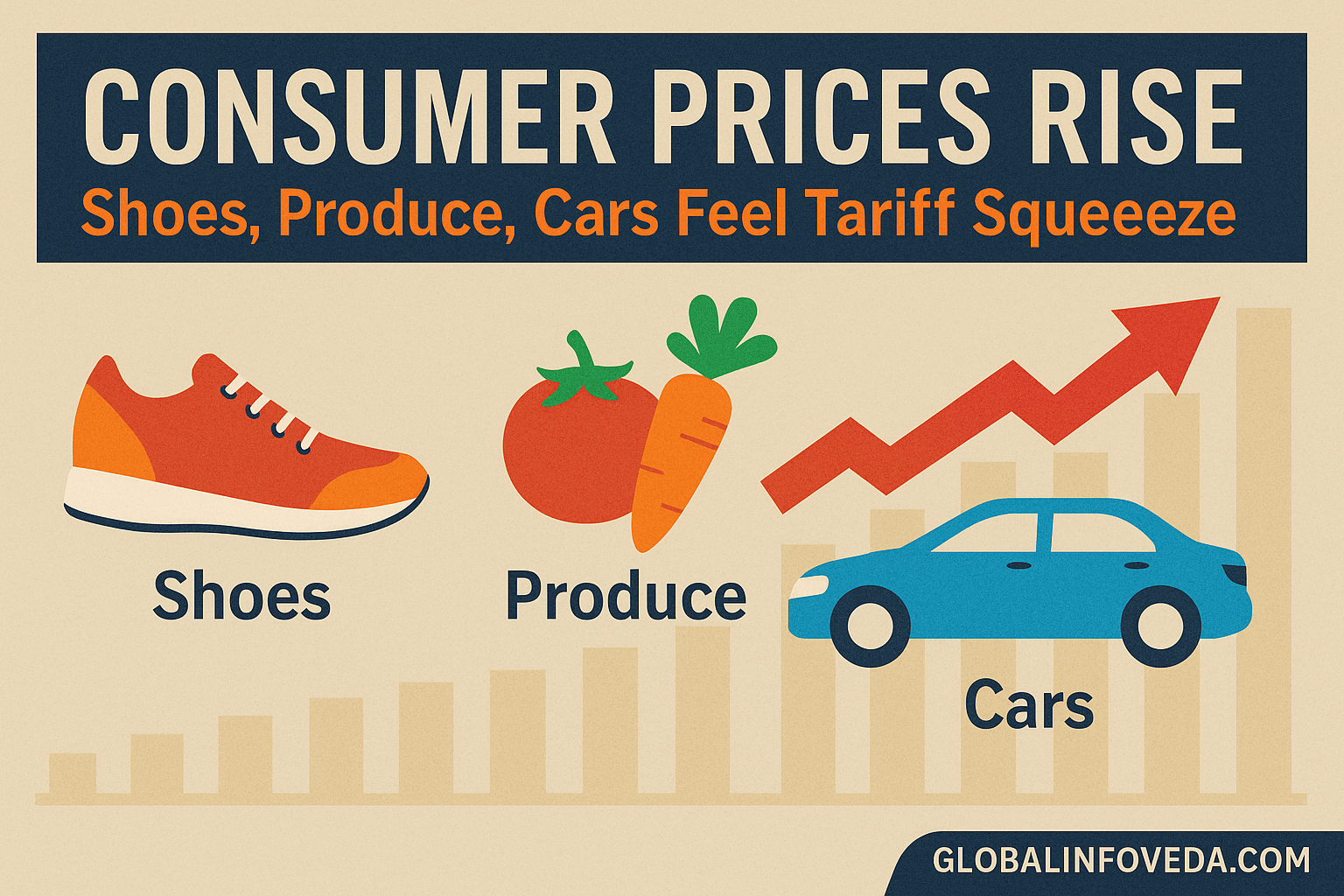
The initial squeeze was felt in sectors with high levels of import intensity and weak pricing power: big‑box retail, specialty apparel, small electrics and mid‑cap auto parts. But the bigger story is the spillover into services. Clinics, salons, logistics, hospitality, and more depend upon imported disposables, equipment boards and packaging go up – when those bills increase, appointment slots lengthen and fee schedules inch up. In technology hardware, backlogs inched higher as boards were re‑sourced to compliant hubs; in industrials, a quarter’s worth of project starts slid as CFOs re‑mapped supply paths. Energy services experienced a softer squeeze, cushioned by commodity exposure if not immune from equipment lead times. The lesser-affected ones were asset-light software, utilities and pieces of insurance, but all of them were not truly insulated because of rising consumer prices and demand elasticity coming into models.
🧮 📊 Trade‑exposure by industry: impact channels
| 🧱 Industry | 🧲 Primary exposure | 🕒 Earnings timing |
|---|---|---|
| Retail / apparel | Landed cost + packaging | Immediate to 2Q |
| Auto components | Sensors, alloys | 1–3Q lag via backlogs |
| Healthcare services | Imported disposables | 2–4Q via fee calendars |
🧰 Portfolio triage — what professionals did in week one
- 🧭 Defend cash flows: emphasize free‑cash‑flow yield over nominal dividend yield; prefer firms with low capex needs and clean working‑capital cycles.
- 🧮 Re‑underwrite demand: re‑score elasticity assumptions; watch entry‑price pegs in mass retail and quick service.
- 🧯 Hedge where it pays: skewed put spreads instead of outright puts when implied vol is frothy; use collars on single‑names with known tariff beta.
- 🧪 Read the specs: any SKU or service with a clear spec card and warranty discipline is better placed to hold share without reputation damage.
- 🧳 Follow the freight: track port dwell, chassis availability, and air‑freight premiums; cost curves predict earnings by sector.
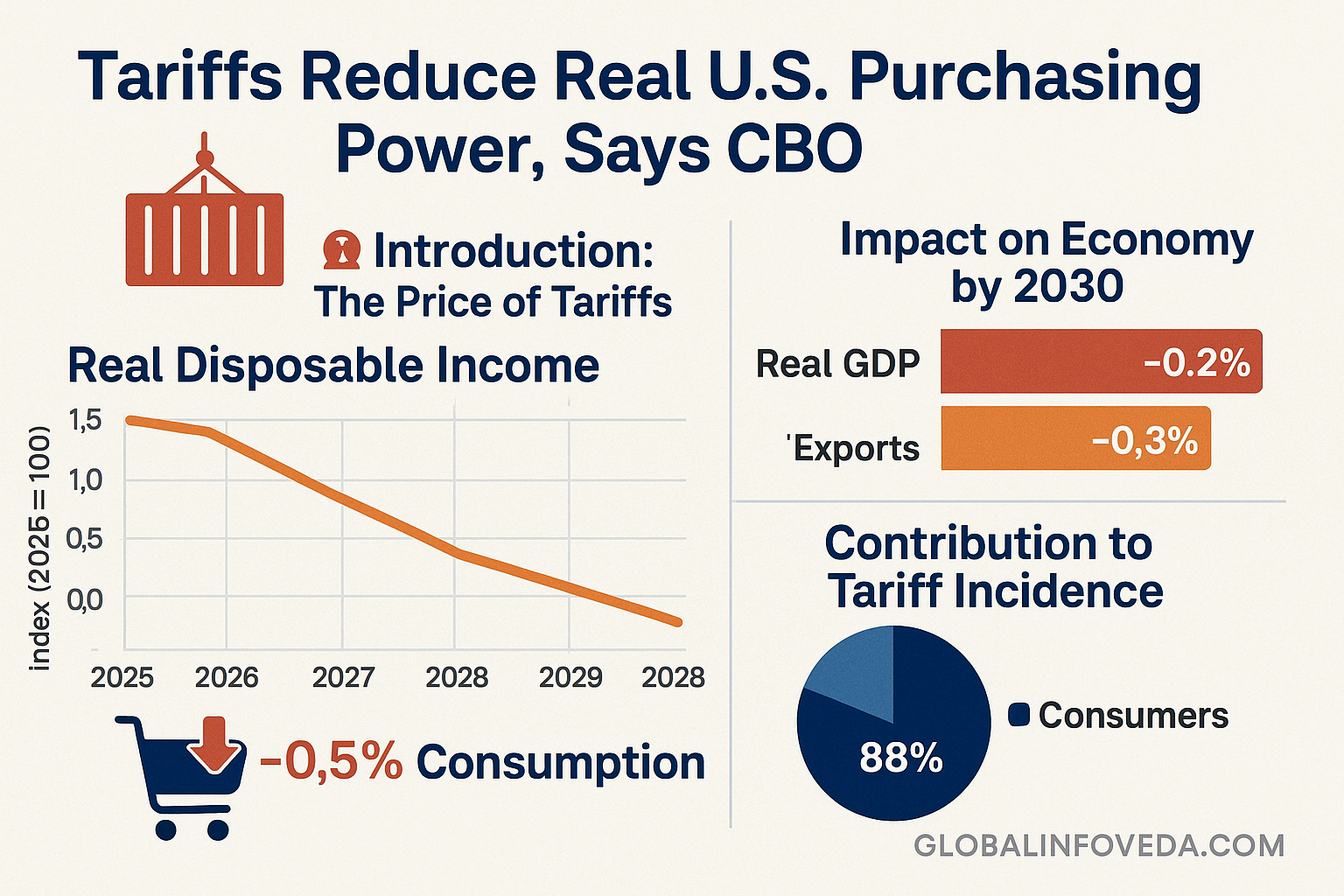
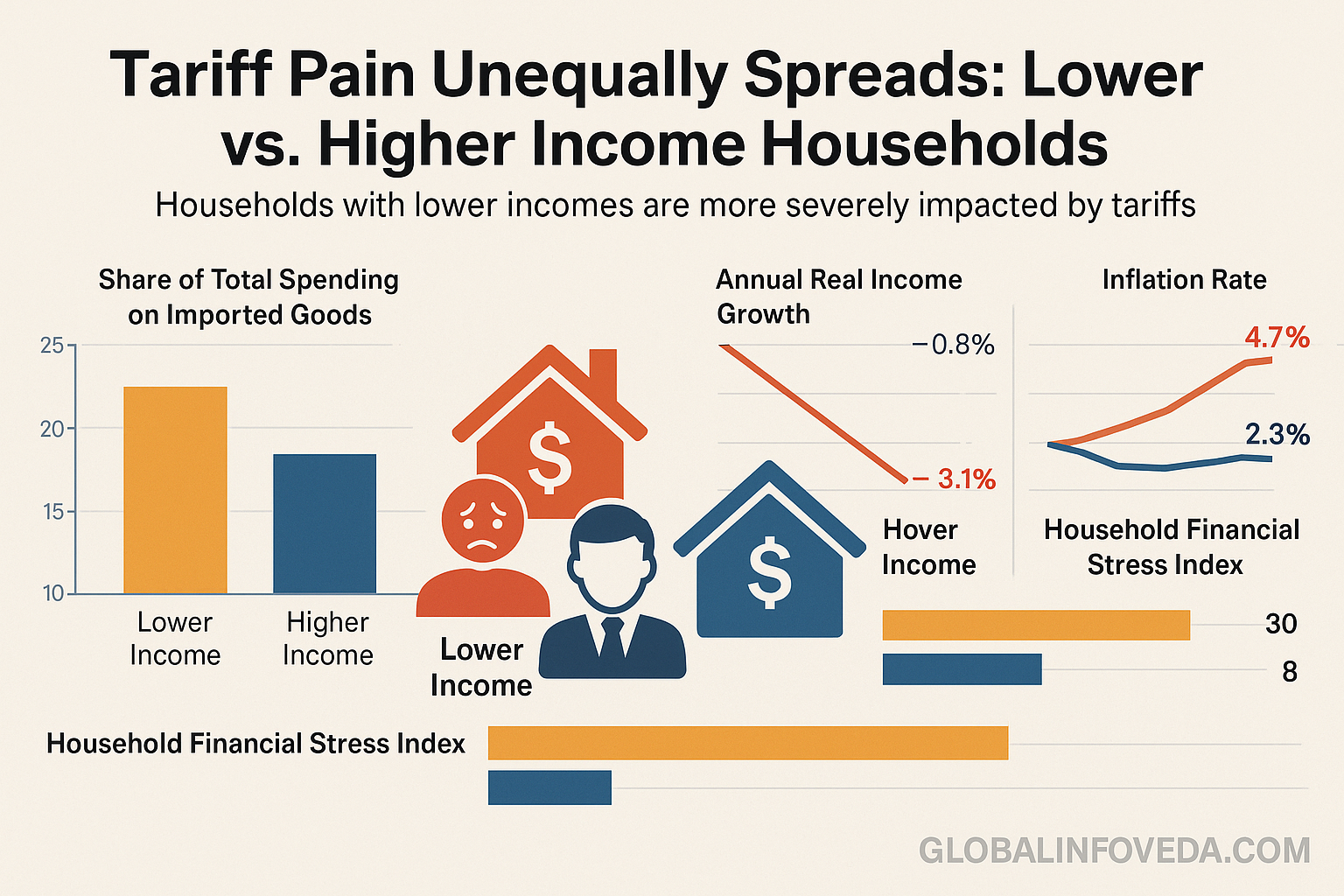
Consumer‑side ripple effects: U.S. Families Could Pay $3,800 More a Year Due to Tariffs
🧠 Microstructure mattered more than headlines
A major factor in the stock market crash 2025 dynamic was market plumbing. As dealers’ books deplete, ETFs in niche themes showed more dislocations; basis trades that normally compress rapidly have yet to do so, a sign that balance‑sheet rationing is in place. Structured products with path‑dependent barriers obliged hedgers to sell into weakness, while stop‑loss bands in retail broker algorithms kicked in and ran through. Meantime, index rebalances intersected with earnings pre-announcements structured around tariff disclosures. The effect was a misleading intraday tape that hid the longer-term, slower reality: a few quarters of a throughput and margins story, not a week of consumption that had been erased.
🧪 Case study — mid‑cap exporter vs. rules‑of‑origin
- 🧭 Problem: a mid‑cap home‑appliance brand assembled in Mexico failed new rules‑of‑origin thresholds due to board sourcing from East Asia.
- 🛠️ Fix: accelerated dual‑sourcing to a compliant hub; redesigned carton specs to raise container fill by 8%.
- 💵 Finance: negotiated longer price locks in exchange for narrower SKU menus; moved from monthly to quarterly volume commitments.
- 🧾 Customer: published a clear materials note and kept the entry‑price peg; introduced optional upgrade packs.
- 🎯 Outcome: base volume held; gross margin recovered within two quarters; brand reputation improved due to transparency.
🌏 Spillovers to India and other emerging markets
That’s because the reality of “Made elsewhere, priced everywhere” meant that tariff pressure ricocheted through supply networks. There were first‑order impacts on India, such as rupee weakness on risk‑off days, portfolio outflows from EM funds rebalancing and valuation compression in export‑oriented mid‑caps. Second‑order effects: There are also potential demand shifts as retailers in the U.S. try friend‑shoring to South and Southeast Asia. The opportunity is real but lumpy: onboarding audits, warranty alignment, and carton math take quarters not weeks. At homes, imported device cycles elongated; and at startups, runway discipline reappeared as cross‑border SaaS renewal met tightened procurement. The joke is on those who want to extract more, but volatility still hurts and execution that’s creditable on compliance and packaging efficiency can turn the window into long-term market share.
🛢️ Energy, metals, and the feedback into services
- ⛽ Fuel surcharges: logistics firms passed bunker and diesel volatility through, raising delivered costs for restaurants and clinics.
- 🪙 Metals drift: aluminum and steel price paths shaped appliance and auto repair quotes; warranty buffers swelled.
- 🧴 Packaging: resin supply inched tighter; refill formats gained traction in personal care and quick service, stabilizing consumer prices at the low end.
- 🧊 Cold chain: reefer availability dictated produce menu stability and small grocer margins.
🏛️ Policy responses that actually move the needle
Smart relief is not about scrapping the policy but tamping down volatility and clearing compliant goods faster. And then there are the tariff‑rate quotas for high-incidence medical and safety disposables, which help even out the hospital fee calendar. “Standards fast‑track” cells speed clearance for vendors who meet documentation criteria, reducing port queues. Public dashboards for port dwell and inspection‑hold rates allow carriers and shippers to self‑correct congestion. And transparency requirements for warranties reduce the temptation to silently degrade the spec. Together, those moves narrow the gap between wholesale cost and shelf price without violating strategic goals.
🌐 How other countries adapted in weeks, not months
- 🇪🇺 Europe: accelerated mutual‑recognition workarounds; leaned on inventory buffers in autos and pharma to smooth delivery promises; state banks nudged supply‑chain finance to lengthen tenors.
- 🇯🇵 Japan: prioritized critical‑component corridors and customs green‑lanes; large firms underwrote SME vendor audits to keep clusters intact.
- 🇸🇬 Southeast Asia: positioned as friend‑shoring hubs; export credit agencies packaged onboarding guarantees; logistics zones marketed milk‑run efficiency.
- 🇲🇽 Mexico: doubled down on origin documentation for North American corridors; near‑shorers co‑invested in testing labs to reduce rework risk.
🧭 Three forward paths — base, upside, and stress
Incrementally, the base case moderates tariffs and provides clarification through quarterly calendars; downgrades continue but narrow into year-end as inventory levels normalize and pricing candor restores throughput. The bull case marries stable policy to above‑trend productivity from carton redesigns, milk‑run routing, and SKU pruning, enabling margin rebuild without needing top‑line heroics. This stress scenario sees more escalation, retaliation and sticky services inflation leading to defensive rotations and balance‑sheet conservatism. From path to path, the trust-holding constant is transparency about specs and warranties so that even as the system is healing, trust is preserved.
🧮 📊 Scenarios at a glance — positioning ideas
| 🧭 Path | 🧰 Operational focus | 🎯 Portfolio tilt |
|---|---|---|
| Base | SKU pruning, spec transparency | Quality defensives, cash‑flow compounders |
| Upside | Carton math, milk‑runs, refurb capex | Re‑risk cyclicals with pricing power |
| Stress | Liquidity buffers, warranty guardrails | Duration, uncorrelated alts, collars |
🧰 Tactics for households and retail investors
- 🧾 Anchor big buys to published promo windows; avoid panic timing.
- 🔧 Run a 12‑week maintenance sprint: filters, seals, tires—prevent the failure premium.
- 📱 Choose certified refurb devices with long OS‑update horizons; avoid mid‑cycle capex shocks.
- 🧴 Adopt refill formats for recurring categories; unit costs fall, packaging stress eases.
- 📊 Use collars on concentrated single‑name exposure rather than selling into weakness if you want to retain upside.
📈 Volatility structure: what options are saying
The volatility term structure also flipped from a mild contango to a small backwardation which, again, was indicative of demand for near‑dated protection. Skew steepened within tariff‑sensitive sectors, and dispersion increased as investors discriminated among operators with strong sourcing discipline and those with opaque disclosures. The lesson for portfolio managers is tactical: buy time on financing protection through call overwrites in names where the upside catalysts are far off; in your quality compounders, look to put spreads to maintain participation while minimizing bleed. Disciplined investors should not be deterred by elevated implied levels; they should focus on risk‑budgeting and put the emphasis on catalysts over calendar noise.
🏦 Funding markets: the quiet stress test
Amid the headline screens, commercial paper and asset‑backed shelves carried a more nuanced story. Large issuers rolled maturities, but smaller import‑dependent firms paid up, widening the divide between scale players and mid‑caps. In bank funding, overnight markets remained orderly but term pricing was cautious. None of this screamed crisis; it was that of a world where working‑capital cycles lengthen and where balance‑sheet buffers become strategy rather than vanity. Boards that rubber‑stamp opportunistic buybacks while windows remain open will be in danger of under‑investing in freight certainty, warranty guardrails and vendor audits – the very levers that ensure throughput.
🧰 Compliance essentials for importers
- 🧾 HS‑code discipline: map SKUs to precise headings; sloppy classification invites punitive adjustment.
- 🧭 Origin documentation: chain of custody must be auditable; invest in digitized certificates and random batch testing.
- 🧪 Specification control: publish spec cards; if you reformulate, disclose and defend function equivalence.
- 📦 Carton optimization: improve container fill via right‑sizing and weight balance; it compounds margin resilience.
- 🔁 Dual‑sourcing: use a lead and lag supplier to keep bargaining power and insure against inspection bottlenecks.
🇮🇳 India’s capital‑market channels
For India, the route in the market was through foreign portfolio flow, rupee sensitivity to risk‑off and the P/E of export‑oriented mid‑caps. But, domestic flows into SIPs in mutual funds and NPS allocations softened the impact. On the ground, friend‑shoring interest quickly built in textiles, electronics and chemicals, but the onboarding costs and audit timelines meant revenue would trail well behind the headlines. Policy windows to monitor were shorter BIS certification queues and customs digitization to ensure compliant cargo kept moving. Credibility is the principal advantage: operators that can prove spec transparency, warranty strength and stable delivery will be banking multi‑year contracts from buyers who want certainty.
🌍 Global indices and ETF mechanics
When sector ETFs trade below net asset value, the market mechanism of arbitrage usually closes the difference. In tariff weeks, balance‑sheet scarcity moderates that snap‑back. Investors who are reading those discounts as a value signal should also look to creation/redemption activity and the liquidity of the underlying baskets. To the extent the authorised participant channel is impeded, discounts can remain without that indicating fundamental mispricing. One observational recommendation: consider using widely diversified vehicles in the first phase of repair, then layer single‑name risk as disclosures clarify sourcing and warranty policies.
🧪 Case study — small clinic network under cost stress
- 🧩 Situation: a 14‑location outpatient network relied on imported consumables and diagnostic spares.
- 🧮 Cost shock: supplier quotes rose 7–10% with uncertain lead times.
- 🛠️ Actions: negotiated tariff‑rate relief for critical disposables; published a transparent fee calendar; adopted refill‑friendly packaging to reduce waste.
- 🧾 Patient trust: communicated warranty terms on devices and standardized spec cards for consumables.
- 🎯 Result: appointment throughput recovered within eight weeks; churn dropped as clarity replaced anxiety.
🛰️ Algorithmic flows: when code meets policy
Intraday flows reflected momentum triggers that exacerbated weakness post- and re-cash announcement as VWAP‑tethered strategies traded. But on day five, mean‑reversion models started nibbling in liquid defensives. This isn’t a mystery; it is a characteristic of capital that is rules‑based and not governed by narrative — capital that is sensitive to volatility and liquidity. Humans who understand these schedules know not to “fight the tape”—but to throw their bids where the liquidity window opens: auction periods, rebalance hours, post‑close periods.
🧠 Media noise vs. operating data
Television had it as a one‑way story of demand evaporating. Operating data hinted at a more nuanced trajectory: Port dwell widened, to be sure, but forward bookings in certain categories held up as buyers prioritized essentials and postponed frills. Warranty claims for white goods increased among vendors reducing specifications in say, ovens; among the most transparent specs, warranty claims remained flat. In services, appointment books stretched rather than disappeared. The moral is to value ledgers and logistics dashboards above sentiment clips.
🧭 30‑60‑90 day roadmaps
- 🗓️ 30 days: publish product and service spec sheets; lock promo windows; renegotiate freight blocks; build a cross‑functional “tariff desk.”
- 🗓️ 60 days: dual‑source critical SKUs; implement carton right‑sizing; convert discrete vendor audits into a rolling calendar.
- 🗓️ 90 days: refresh pricing architecture; introduce refurb and repair lanes; codify warranty and returns to harden trust.
🔍 Red flags and green shoots
- 🚩 Red flags: opaque spec changes; widening inspection‑hold times without explanation; erratic promo calendars; rising returns.
- 🌱 Green shoots: declining port dwell; increasing container fill; transparent spec cards; steady appointment throughput in services.
🧭 What would invalidate the bear case?
A sustainable inflection would probably combine a cessation of tariff pressure with evidence that operators can preserve entry‑tier value in a fair way. Tangible signals: steady inspection‑hold rates regular warranty claim ratios, and freight premiums rolling off. If those do arrive, as this currently elongated labour cycle persists and household consumer prices stop falling, equity multiples could recover before even revenue growth picks up. That’s not optimism for the sake of optimism; it is an execution‑led recovery thesis.
❓ FAQs
- Will equities rebound quickly once policy clarity arrives? The tactical bounce can be fast, but sustained recoveries depend on throughput normalizing—watch port dwell, warranty claims, and retailer promo calendars.
- Are defensives immune? No. services with imported inputs still see fee pressure; the advantage is pacing and transparency, not invisibility.
- Is it wiser to shift entirely to domestic suppliers? Blend instead. Dual‑sourcing plus warranty clarity lowers risk without exploding cost.
- How do I tell good value from stealth shrink? Demand spec cards, unit measures, and warranty details; reward providers who publish them.
📚 Sources
- U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) — CPI, PPI, and services price trends: https://www.bls.gov/
- U.S. International Trade Commission / Office of the USTR — tariffs, investigations, and rulings: https://www.ustr.gov/
- Institute for Supply Management (ISM) — Services PMI and new orders indexes: https://www.ismworld.org/
- International Monetary Fund (IMF) — World Economic Outlook chapters on trade and spillovers: https://www.imf.org/
🌟 Final Insights
The “Liberation Day” tariffs have not only ruined a trading day — they also exposed the hidden gears between policy and equity markets, households and Main Street outfits. The cure, in the near‑term, is not macho but craft: spec transparency, warranty discipline, milk‑run logistics, carton math, and honest entry‑tier scopes that preserve trust while costs normalize. Investors must ignore theater and being tracking the boring but telling numbers — port dwell, container fill and promo calendars — that lead actual earnings by a quarter or two. If policymakers, in a sense, time‑box the relief and could operators speak as partners, then the stock market crash 2025 becomes an overpass to process maturity, not a cul‑de‑sac of higher consumer prices.
👉 Explore more insights at GlobalInfoVeda.com